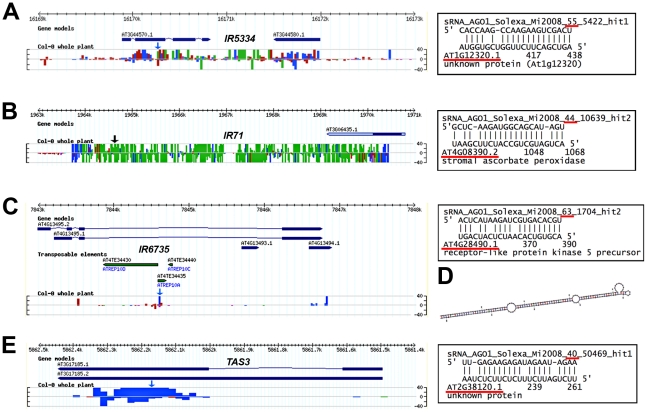
Figure 2. Using the AGO1-IP read filter in conjunction with VSR microarray data uncovers possibly novel IR- andTAS-derived siRNA target transcripts with altered accumulation by VSRs.
(A-E) Left panels provide ASRP genome browser views of the small RNA loci of origin. Colored arrows indicate the position and length of the small RNA. Blue, green and red labels indicate 21nt-long, 22nt-long and 24nt-long siRNA species, respectively. A black color signifies small RNAs with length diverging from the above. The right panels depict predicted target sites alongside the small RNA identification number (as in [30]), AGO1-IP read value (underlined in red) and number of loci of origin (hit). The gene identification number of the predicted target is underlined in red. (A–C) Inverted-repeat (IR)-derived siRNAs and their predicted targets, At1g12320 (in leaves; A), At4g08390 (in stems and leaves; B) and At4g28490 (in stems and leaves; C). (D) Predicted secondary structure of the transposon-derived IR6735. (E) A 21nt-long siRNA derived from the TAS3 locus predicted to target the At2g38120 transcript in leaves. For each example, statistically significant up-regulation of gene expression was validated in two independent qRT-PCR analyses of total RNA extracted from the indicated tissues.