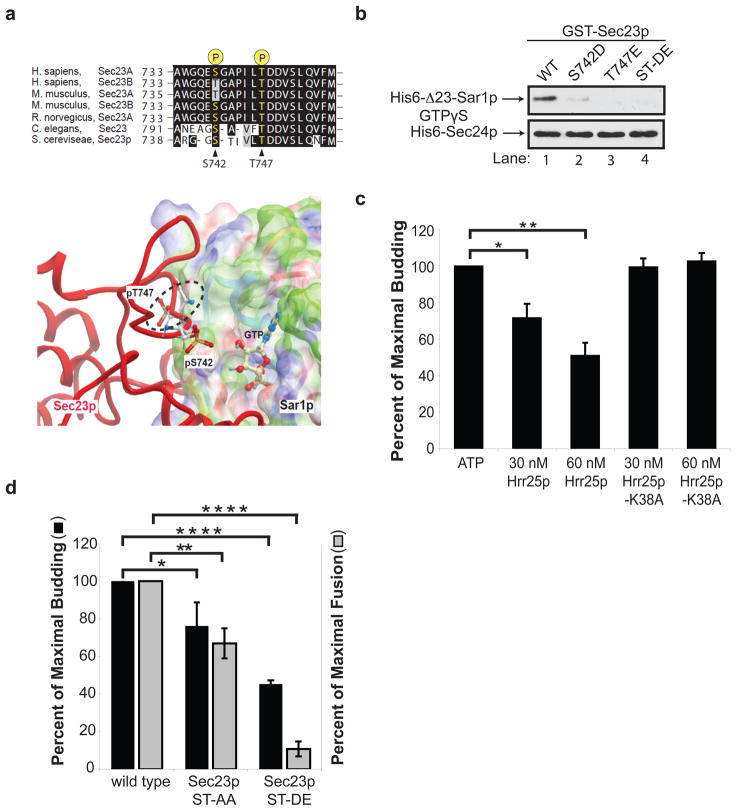
Figure 3. Phosphorylation of S742 and T747 blocks ER-Golgi traffic in vitro.
a, Top, The sequence flanking S742 and T747 in Sec23p was aligned with Sec23 orthologues. Bottom, Phosphorylated S742 and T747 in Sec23p (red) are located at its interface with Sar1p. The electrostatic potential of the Sec23p-binding surface of Sar1p is colored according to solvation properties of the residues (white, hydrophobic; green, polar; blue, basic; red, acidic). The dotted ellipsoid marks the steric clash between Sec23p and Sar1p-GTP. b, Top, wild type (WT) and mutant GST-Sec23p fusion proteins were incubated with 10 nM of His6-Δ23-Sar1p-GTPγS or His6-Sec24p. A truncated form of Sar1p was used for these studies because the full length protein aggregates15. c, Increasing amounts of purified His6-Hrr25p or His6-Hrr25p-K38A were added in vitro at the beginning of a complete transport reaction and vesicle budding was measured. Error bars represent S.D., N=4. d, Fractions prepared from the indicated strains were assayed for vesicle budding and fusion as before6. Error bars represent S.E.M., N=4 (*P<0.05, **P<0.01,, ****P<0.0001 Student’s t test).