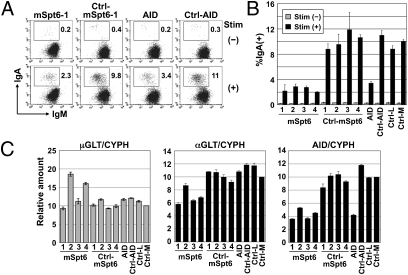
Fig. 2.
CSR is inhibited by Spt6 knockdown in CH12F3-2A cells. (A and B) Spt6 knockdown severely reduced CSR efficiency. CH12F3-2A cells (1.5 × 106) were introduced with 1.5 μg of siRNAs against mSpt6, scrambled siRNA for them, an siRNA against mAID, a scrambled siRNA for it, or negative control siRNAs with low (36%) and medium (48%) GC contents (Ctrl-L and Ctrl-M, respectively). The GC contents of oligos mSpt6-1, -2, and -4 are medium (45–55%), and those of oligos mSpt6-3 and AID are low (35–45%). Twenty-four hours after siRNA introduction, cells were stimulated with CD40L, IL-4, and TGF-β for 24 h. The percentages of IgA+ cells in the live population are indicated. Representative FACS profiles are shown (A). The mean ± SD values were obtained from triplicate experiments (B). (C) siRNAs against Spt6 reduced the amount of αGLT and AID transcripts. Quantitative PCR analyses for μGLT, αGLT, and AID transcripts in Spt6-knockdown cells. Values were normalized by cyclophilin (CYPH). Unstimulated and stimulated cells were analyzed for μGLT and for αGLT and AID transcripts, respectively.