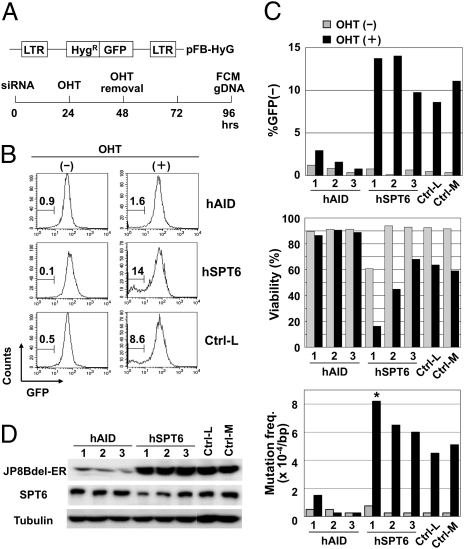
Fig. 5.
Spt6 knockdown augmented SHM in BL2 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the artificial SHM substrate and the SHM assay procedure. BL2 cells expressing JP8Bdel-ER and the artificial SHM assay substrate were introduced with siRNAs, stimulated for 24 h with OHT, and incubated for an additional 48 h in the absence of OHT. Then cells were harvested for flow cytometry (FCM) and genomic DNA extraction. (B and C) SPT6 knockdown augmented the SHM efficiency in the artificial substrate. BL2 cells expressing JP8Bdel-ER and the artificial SHM assay substrate (1.5 × 106) were introduced with 3.0 μg of siRNAs against hSPT6, siRNAs against hAID, or negative control siRNAs with low (36%) and medium (48%) GC contents (Ctrl-L and Ctrl-M, respectively). The GC contents of oligos hAID-1, -2, -3, and hSPT6-3 are medium (45–55%) and those of oligos hSPT6-1 and -2 are low (35–45%). The percentages of GFP− cells are indicated (B). Graphical summary of the percentages of GFP− cells, viability, and mutation frequencies in the GFP sequence (C). Statistical significance was evaluated against the corresponding control oligo by χ2 test. *P < 0.05. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Two siRNA oligos against SPT6 (1 and 2) reduced the amount of SPT6 protein but did not affect the amount of JP8Bdel-ER protein. Note that the other siRNA oligos against SPT6 (3) did not substantially reduce the amount of SPT6 protein.