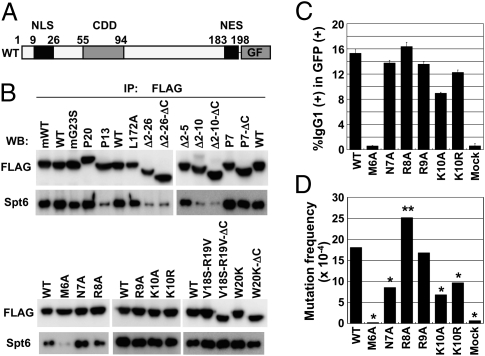
Fig. 6.
AID interacts with Spt6 through its N terminus. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant AID-GF constructs. (B) Western blot analyses of immunoprecipitates with anti-FLAG from cytosolic extracts of CH12F3-2A cells expressing wild-type AID-GF or mutant AID-GFs. All AID constructs are of human origin except for mWT and mG23S. An equal amount of wild-type and mutant AID-GF proteins was analyzed by adjusting the loading amounts of immunoprecipitates. (C) AID-deficient splenocytes were stimulated with LPS for 48 h and infected with retroviruses expressing mutant AID-GFs. Cells were stimulated for additional 48 h in the presence of LPS and IL-4. The percentages of IgG1+ cells in the GFP+ population are indicated. Mean ± SD values were obtained from triplicate experiments. (D) NIH 3T3 cells harboring an SHM substrate pI were infected with retroviruses expressing wild-type and mutant AID-GFs and cultured for 7 d. Genomic DNA was extracted for sequencing analysis. GF was used as mock. Statistical significance was evaluated against WT by χ2 test. *P < 0.001, **P < 0.05.