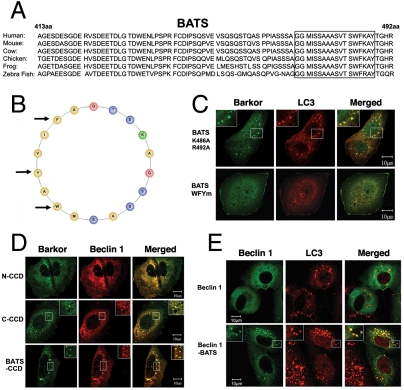
Fig. 2.
The amphipathic alpha helix of BATS is responsible for autophagosome membrane binding. (A). The last 80 amino acids (BATS) of Barkor/Atg14(L) homologues in vertebrates were aligned, and a highly conserved membrane interaction helix was predicted and noted by a box. (B). The predicted membrane interaction helix is presented as an amphipathic helical wheel. Hydrophobic residues are yellow, the hydrophilic residues are blue, and positively charged residues are green. Three hydrophobic residues mutated in C are marked by arrows. (C). Cells stably expressing Myc-LC3 were coexpressed with different BATS mutants, which were tagged with hrGFP (BATS K486A, R492A and BATS WFYm-BATS mutant W484R, F485R, Y488R). Cells were treated with 200 μM CQ for 2 h and stained with c-Myc antibody for LC3 and green fluorescence for BATS mutants. (D). U2OS cells were coexpressed with Myc-Beclin 1 and different Barkor/Atg14(L) mutants tagged by hrGFP and treated with 200 μM CQ. (E). Cells stably expressing Myc-LC3 were coexpressed with either GFP-Beclin 1 or GFP-Beclin 1-BATS, and treated with 200 μM CQ for 2 h.