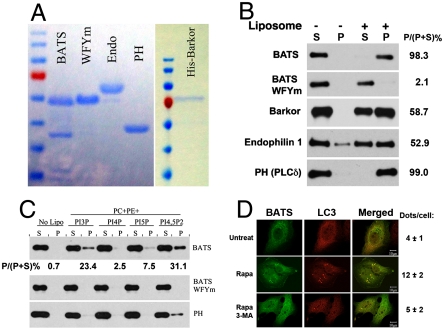
Fig. 4.
Membrane binding activity of the BATS domain. (A). GST-tagged constructs of wild-type BATS, BATS WFYm mutant, endophilin 1, and PH domain of PLCδ were recombinantly expressed and purified from E.coli. Full-length His-tagged Barkor/Atg14(L) was expressed and purified from baculovirus-infected insect cells. (B). Purified recombinant proteins described in A were tested for their liposome binding activity in a cosedimentation assay. Liposomes generated from Folch fraction I of brain extract from bovine brains were used in this assay. S denotes supernatant and P denotes pellet. The binding efficiency is calculated as bound proteins (P) versus input (P + S). (C). Recombinant wild-type BATS, BATS WFYm mutant and the PH domain of PLCδ were incubated with liposomes incorporated with different forms of phosphoinositides and tested for their liposome binding in a cosedimentation assay. S denotes supernatant and P denotes pellet. (D). Cells expressing GFP-BATS and Myc-LC3 were left untreated, treated with Rapamycin alone or in combination with 3-Methyladenine (3-MA), and observed under the fluorescence microscope. Dots per cells were calculated in at least 50 cells from three independent experiments.