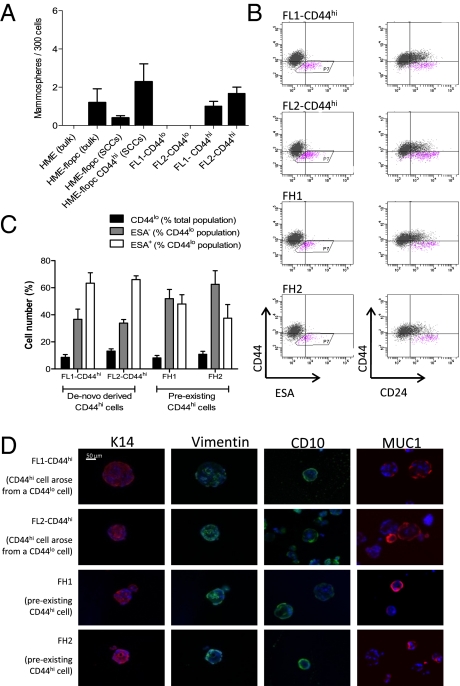
Fig. 3.
CD44hi cells display stem-like properties in vitro. (A) Mammosphere-forming ability of bulk HME or HME-flopc cells, HME-flopc-CD44lo single-cell clones (SCCs, n = 5), HME-flopc-CD44hi SCCs (n = 4), and CD44hi and CD44lo cells purified by FACS from two independent HME-flopc SCCs (FL1 and FL2). Results are mean ± SEM. (B) Representative flow cytometry plots for the markers CD44, CD24, and ESA of cells isolated from dissociated mammospheres from de novo-derived CD44hi cells (FL1-CD44hi and FL2-CD44hi) and two stable HME-flopc-CD44hi SCCs (FH1 and FH2). (C) Quantification of total CD44lo cells, CD44loESA− and CD44loESA+ populations [from (B) box P7; n = 3]. Results are mean ± SEM. (D) Frozen sections of mammospheres (5 μm) stained by immunofluorescence for myoepithelial [CD10, vimentin, and cytokeratin-14 (K14)] and luminal (K14 and MUC1) differentiation markers.