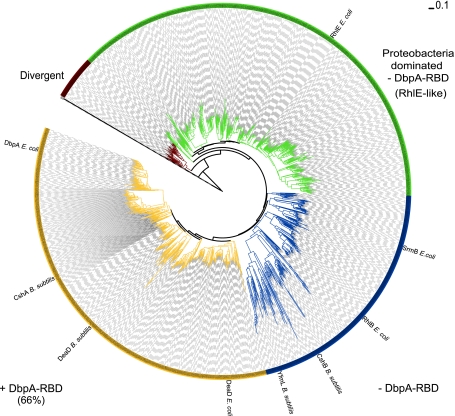
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of the DEAD-Helicase_C domains in 1211 bacterial DEAD-box proteins. Sequences containing only DEAD and Helicase_C domains were first aligned and then manually curated. We used Gblocks to extract informative positions from the protein alignment and a total of 323 non-ambiguous positions were used to conduct the phylogenetic analysis by Neighbor joining (see “Materials and methods”). The grouping of classes was determined according to clades layout. Three major groups are identified and colored yellow, blue, and green. Some Actinobacteria DEAD-box protein sequences branch in a separate divergent group (brown). The presence and absence of a DbpA RNA-binding domain (RBD) is the main feature distinguishing yellow and blue DEAD-box protein sequences, respectively, while green section sequences form a separate branch that is dominated by proteobacterial members. Location of known RNA helicases from E. coli and B. subtilis are indicated in the phylogeny. Information about the genomes and the sequences IDs used to generate this phylogeny can be found in Supplemental Tables S4 and S5