Figure 1.
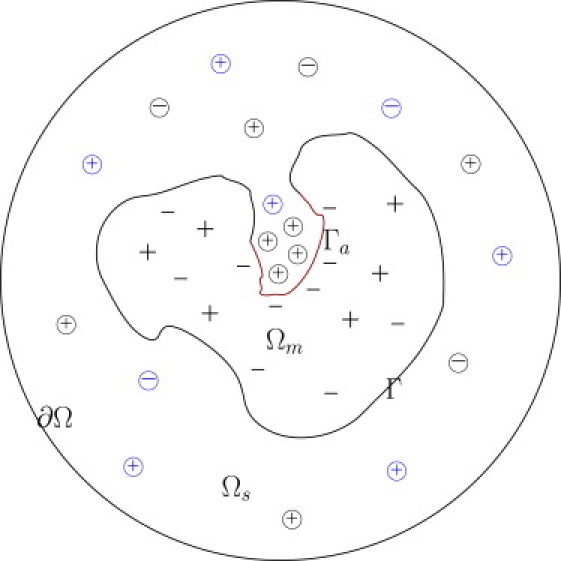
Two-dimensional schematic illustration of the computational domain modeling a solvated biomolecular system. The biomolecule(s) is located in domain Ωm and the aqueous solution is in domain Ωs. The molecular surface is Γ. The active reaction center Γa ⊂ Γ is highlighted in red. The circles of different colors with plus or minus sign inside represent the diffusive charged particles of different species that have finite sizes and move only in Ωs. The singular charges inside molecules are signified with plus or minus sign in Ωm. The minimum distance between the molecular surface Γ and the exterior boundary ∂Ω is much larger than the diameter of the molecule so that approximate boundary condition for the electrostatics can be applied.
