Figure 8.
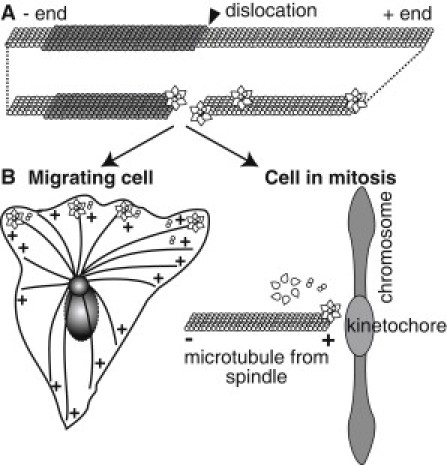
Illustration of proposed GFP-Katanin-60 activities in vitro and in the cellular context. (A) The GFP-Katanin-60 assembles as a hexamer in the presence of ATP, and associates with defects in the lattice, such as protofilament shifts and MT ends. Once GFP-Katanin-60 binds, it rapidly removes dimers from active sites at plus ends and at defects. (B) In the cell, the same katanin could regulate MT plus ends to alter length and dynamics at the leading edge of migrating cells or at the kinetochores in the mitotic spindle.
