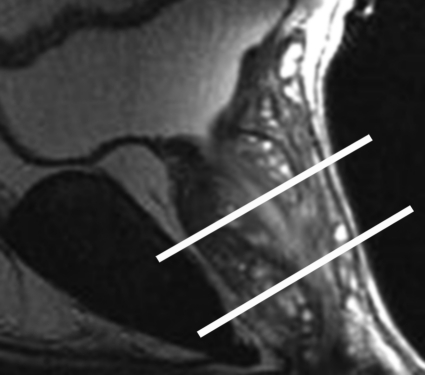
Figure 2a.
Anatomy of the prostate on endorectal MR images obtained at 1.5 T. (a) Sagittal T2-weighted image (repetition time msec/echo time msec = 3350/92) shows division of the prostate into three sections in the craniocaudal direction. The superior one-third of the prostate below the bladder is the base. The middle one-third is the midgland. The distal one-third is the apex. (b) Axial T2-weighted image (6000/92) shows the base of the prostate. The anterior fibromuscular stroma (arrow) consists of nonglandular tissue and appears dark. Note the symmetric homogeneous muscular stroma layer (arrowheads) in the posterior prostate base. (c) Axial T2-weighted image of the midprostate shows the homogeneously bright peripheral zone (arrowheads) surrounding the central gland (white arrows). The central gland is composed of the transition zone and central zone, which cannot be resolved at imaging. Therefore, they are referred to jointly as the central gland. Note the neurovascular bundles at the 5-o'clock and 7-o'clock positions (black arrows). (d) Axial T2-weighted image of the prostatic apex shows the homogeneous peripheral zone (arrowheads) surrounding the urethra (U). Note that the volume of the peripheral zone increases from the base to the apex.