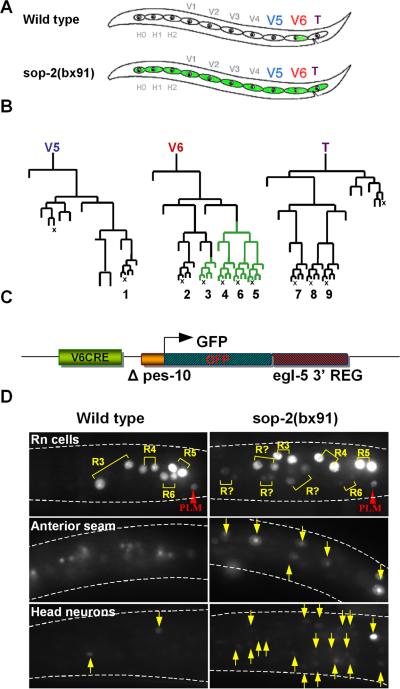
Fig. 1.
The expression domain of a minimal egl-5 seam cell reporter gene is restricted by sop-2. A. Seam cells in an L1 larva. Seam cells form a row of hypodermal blast cells that generate additional hypodermal cells and neurons during postembryonic development. The three posterior seam cells V5, V6, and T generate the male rays. The wild type egl-5 gene is expressed in the posterior lineage branches of V6. In a sop-2 mutant, it is expressed in more anterior seam cell lineages as well. B. Postembryonic cell lineages of seam cells V5, V6 and T in the male. egl-5 is expressed in the posterior branches of the V6 lineage beginning in the L2 larval stage (green lineage branches). The terminal sublineages labeled 1-9 generate the rays (X, programmed cell death). C. Structure of the minimal egl-5 seam cell reporter, V6CRE-egl-5-3’REG. In this reporter, GFP transcribed from the C. elegans promoter Δpes-10 is controlled by the egl-5 V6 lineage cis regulatory element V6CRE and egl-5 3’ DNA. D. Expression of V6CRE-egl-5-3’REG in the anterior seam is repressed by sop-2. In wild type, shown is GFP fluorescence in the first two daughters of the ray precursor cells (Rn cells), R3, R4, R5, and R6, which generate the ray sublineages leading to rays 3-6. Flurosecence is also present in the posterior touch cell PLM. The reporter is not expressed in the anterior seam (background fluorescence is due to gut autofluorescence), and has weak expression in a few head neurons (arrows). In sop-2(bx91), additional ray sublineages express the reporter, as well as anterior seam cells and additional head neurons (arrows).