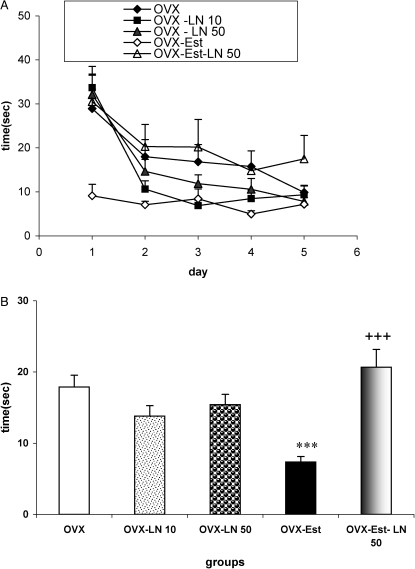
Figure 1.
Comparison of the latency among the OVX, OVX-LN 10, OVX-LN 50, OVX-Est and OVX-Est-LN 50 groups. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. (n = 8 in each group).The OVX-LN 10 and OVX-LN 50 groups were treated with daily injections of 10 and 50 mg/kg L-NAME, respectively, from the day after ovariectomy until the beginning of the behavioral study. The animals in the OVX-Est group were treated with weekly injections of estradiol valerate (2 mg/kg; i.m.). The animals in the OVX-Est-LN 50 group were treated with weekly injections of estradiol valerate (2 mg/kg; i.m.) and received daily injections of 50 mg/kg L-NAME. There were no significant differences in the latency between the OVX-LN 10 and OVX-LN 50 groups and the OVX group; however, the animals in the OVX-Est group had a significantly lower latency and time to reach the hidden platform than the OVX group (p<0.001). In the OVX-Est-LN 50 group, the latency was significantly higher than in the OVX-Est group (p<0.001). *** p<0.001 compared to OVX group; +++ p<0.001 compared to OVX-Est group.