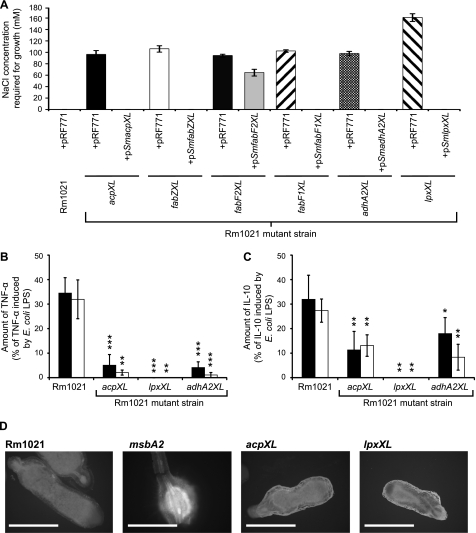
FIGURE 4.
The S. meliloti acpXL-lpxXL mutants have a minimum salt requirement for growth, and their LPS is less immunogenic than the parent strain LPS. A, the S. meliloti parent strain with the control plasmid (pRF771) or the mutant strains with either pRF771 or the respective complementing plasmid were streaked onto a gradient of LB−NaCl supplemented with NaCl ranging from 0 to 500 mm. The minimum salt concentration for growth was determined assuming a linear salt gradient across the agar. The absence of a bar indicates that the strain grows in the absence of sodium chloride. B and C, human monocytes from two individuals were exposed to 1 μg/ml purified LPS from the defined strains, and then the amount of TNF-α (B) and IL-10 (C) in the supernatant was determined after 6 h of incubation. The cytokine amounts shown are expressed as a percentage of the cytokine induction by E. coli LPS, which induced TNF-α and IL-10 levels from human monocytes of 973.2 ± 73.0 and 228.1 ± 34.3 pg/ml for individual 1 (filled bars) and 2241.3 ± 216.4 and 291.6 ± 27.5 pg/ml for individual 2 (open bars), respectively. The significance values (***, p ≤ 0.001; **, p ≤ 0.01; *, p ≤ 0.05) represent comparisons of the individual LPS responses induced by the mutant strains relative to the S. meliloti parent strain. D, the autofluorescence of plant defense polyphenolics in alfalfa nodules infected with the designated strains was determined using fluorescent microscopy. The nodules from five different alfalfa plants for each strain were analyzed, and representative nodules images are shown. Scale bars, Rm1021, acpXL, and lpxXL (2 mm) and msbA2 (1 mm). Error bars, S.D.