FIGURE 1.
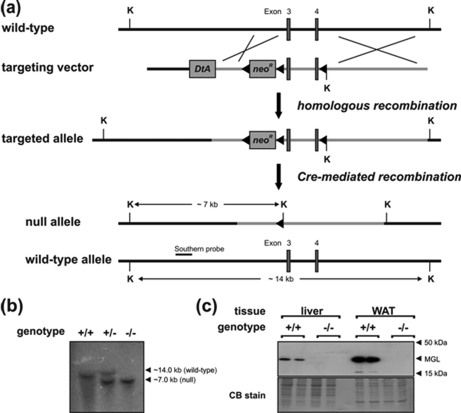
Targeting strategy and generation of MGL-ko mice. a, homologous recombination of the targeting vector with the wild-type allele resulted in the introduction of a loxP site (◀) into intron 4 and a neomycin resistance gene cassette flanked by loxP sites into intron 2 of the MGL gene. Subsequent Cre-recombinase-mediated recombination among the distal loxP sites resulted in the deletion of exon 3 and 4 of the MGL gene. The targeted allele was identified by KpnI (K) restriction digest and hybridization with an external Southern probe (solid bar) revealing a 7.0-kb DNA fragment. b, genomic DNA from mice was digested with KpnI and analyzed by Southern blotting using an external probe specific for intron 2 of the MGL gene. Autoradiography signals obtained from DNA fragments of 14.0 and 7.0 kb corresponded to wild-type (+) and targeted MGL (−) alleles, respectively. c, Western blotting analysis of MGL protein expression levels was performed with lysates of WAT and liver using a rabbit polyclonal MGL antiserum. The polyvinylidene fluoride membrane was stained with Coomassie Blue (CB) as loading control.