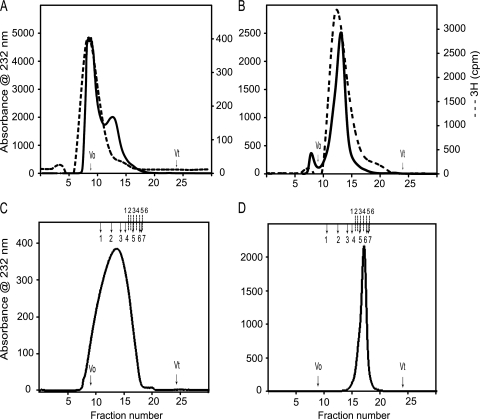
FIGURE 1.
High performance size exclusion chromatography of liver heparan sulfates. A Dionex HPLC system was used to equilibrate a prepacked Superdex 75 HR column (10 × 300 mm; GE Healthcare) at 0.5 ml/min in 10 mm HEPES buffer, 150 mm NaCl (pH 7.2). The anion exchange chromatography-purified liver HS samples were fractionated to check the intact full chains. Then the high molecular weight 3H-labeled male liver HS chains (A) and low molecular weight 3H-labeled female liver HS chains (B) were separated and run again on the same column to confirm the homogeneity. The male liver HS (C) and female liver HS (D) were run on the Superdex 200 HR column (10 × 300 mm) to check the size of the HS chain. The Superdex 200 column was calibrated using gel filtration high and low molecular weight protein calibration marker proteins and even-numbered heparin oligosaccharides derived from heparin. The column void (V0) and total (Vt) volumes were determined using blue dextran 2000 and sodium dichromate, respectively. The elution volumes (Ve) of protein standards were converted into a calibration chart of Kav against molecular mass (Kav = (Ve − Vo)/(Vt − Vo). A line of best fit was fitted to the calibration data using Microsoft Excel, and the equation of this line was used to estimate mass according to observed Kav. The total number of disaccharide repeats was calculated based on the elution position of the known heparin oligosaccharides (dp2–dp26). The completed arrows indicate the elution positions of high and low molecular weight protein standards (1, ferritin; 2, aldalose; 3, conalbumin; 4, ovalbumin; 5, carbonic anhydrase; 6, ribonuclease A; 7, aprotinin), and the dotted lines indicate the elution positions of heparin oligosaccharide standards (1, dp26; 2, dp20; 3, dp16; 4, dp12; 5, dp8; 6, dp6).