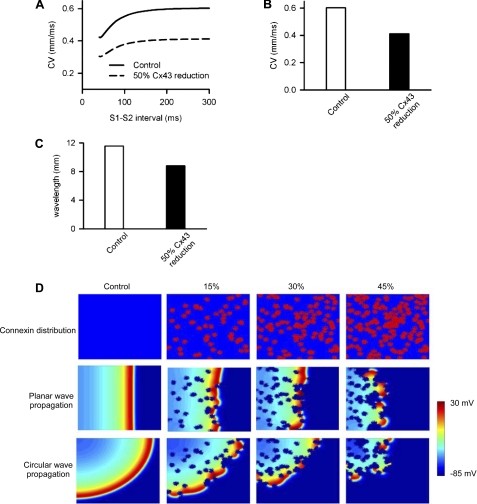
FIGURE 6.
Computational simulations of the effects of Cx43 remodeling on increased propensity for arrhythmias. A, CV under control (solid line) and 50% homogeneous reduction of Cx43 (dashed line). B, conduction velocity when the S1-S2 interval is equal to 100 ms. C, the effect of reduced Cx43 coupling on wavelength of a solitary wave. D, effects heterogeneous reduction of gap junctional coupling on the propagation of ventricular excitation waves in a two-dimensional model of the ventricular sheet. The top rows show a color-coded distribution of gap junctional coupling (blue, D = 0.011 mm2/ms; red, D = 0), the middle and bottom rows show snapshots of planer wave conduction and circular wave conduction, respectively. Snapshots of ventricular excitation wave conduction were shown for the control conduction (first columns), a 15% reduction of the gap junctional coupling (second columns), a 30% reduction (third columns), and a 45% reduction (fourth columns).