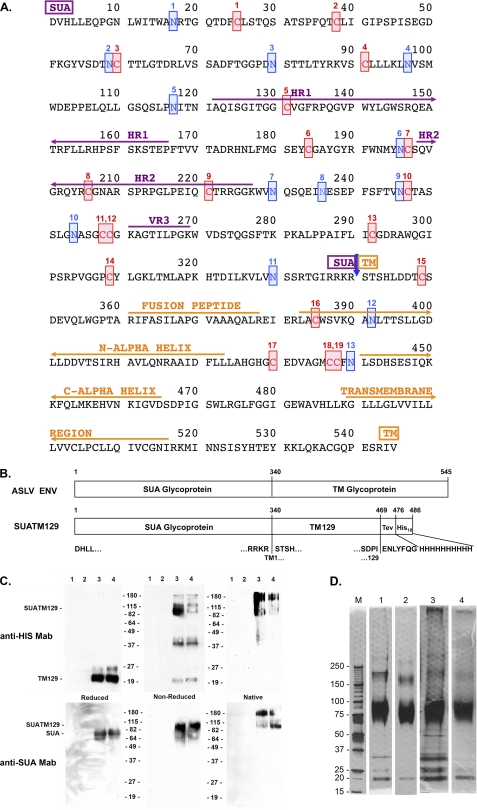
FIGURE 1.
Amino acid sequence of the mature subgroup A ASLV envelope glycoprotein and analysis of the purified SUATM129 glycoprotein. A, functional regions of SUA, hr1, hr2, and vr3 primarily responsible for interacting with the Tva receptor, TM, the internal fusion peptide domain, the N- and C-α helices and the transmembrane domain, are indicated. The 19 cysteine residues are numbered and highlighted in red. The 13 possible N-linked glycosylation sites are numbered and highlighted in blue. SUA and TM are cleaved after amino acid 340 (blue arrow). B, schematic representations of the mature wild-type ASLV(A) and SUATM129 envelope glycoproteins. The TEV protease cleavage site and the His10 tag are shown fused to TM residue 129. C, Western immunoblot analysis of SUATM129 purified from two negative cell lines (lanes 1 and 2) and two cell lines expressing SUATM129 (lanes 3 and 4). Samples were either left nonreduced or reduced with β-mercaptoethanol and separated by SDS-PAGE, or left in the native state and separated by PAGE using Criterion 4–15% gradient gels. The proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose and the Western immunoblots probed first with either an anti-His or anti-SUA monoclonal antibody, and then a peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. The bound complexes were visualized by chemiluminescence. Molecular mass markers are in kDa. D, SDS-PAGE analysis of two different purified SUATM129 preparations (preparation 1 in lanes 1 and 2; preparation 2 in lanes 3 and 4). Nonreduced SUATM129 samples after metal affinity purification (lanes 1 and 3) or after metal affinity plus octyl-Sepharose purification (lanes 2 and 4) were separated by SDS-PAGE using Criterion 4–15% gradient gels. The proteins were visualized with silver stain. Molecular mass markers (lane M) are in kDa.