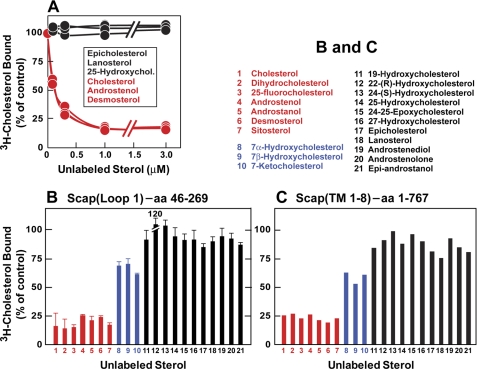
FIGURE 4.
Comparison of the sterol specificity of [3H]cholesterol binding to Scap(Loop1) and Scap(TM1–8). A and B, competitive binding of unlabeled sterols to His6-Scap(Loop1). Each reaction, in a final volume of 100 μl of buffer C with 0.004% Nonidet P-40 and 0.001% Fos-choline 13, contained 5 pmol of His6-Scap(Loop1), 1 μg of bovine serum albumin, 150 nm [3H]cholesterol (222 dpm/fmol), and either varying concentrations of the indicated unlabeled sterol (A) or a 1.5 μm concentration of the indicated unlabeled sterol (B). After 4 h at room temperature, bound [3H]cholesterol was measured by the Ni2+-NTA-agarose assay, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each value represents total binding without subtraction of blank values and is the average of duplicate (A) or triplicate (B) assays. The “100% of control” values, determined in the absence of unlabeled sterols, was 398 fmol/tube and 673 fmol/tube in A and B, respectively. C, competitive binding of unlabeled sterols to His10-Scap(TM1–8). These data are replotted from Fig. 3D of Radhakrishnan et al. (1). Briefly, each assay tube, in a final volume of 100 μl of buffer E with 0.1% Fos-choline 13, contained 120 nm His10-Scap(TM1–8), 100 nm [3H]cholesterol (120 dpm/fmol), and a 5 μm concentration of the indicated sterol. After 4 h at room temperature, the amount of bound [3H]cholesterol was determined by the Ni2+-NTA-agarose assay. The “100% of control” values, determined in the absence of unlabeled sterols, ranged from 209 to 263 fmol/tube. No blank values were subtracted. Each data point is the average of duplicate assays. aa, amino acids.