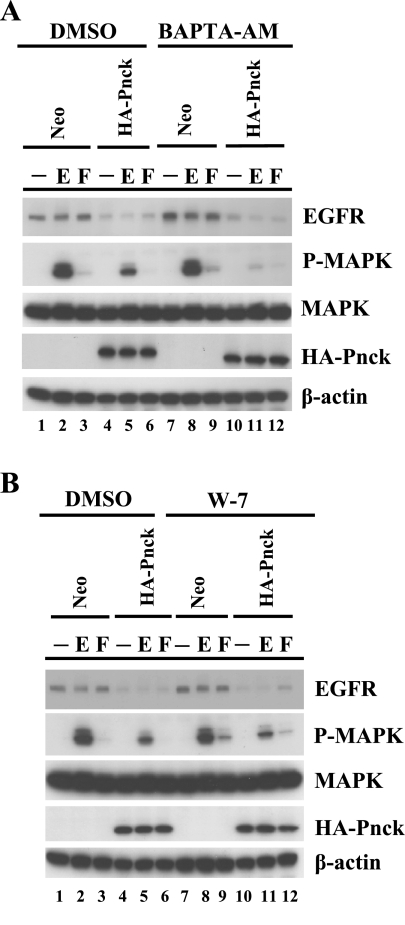
Fig. 1.
Pregnancy-upregulated nonubiquitous calmodulin kinase (Pnck)-induced ligand-independent epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) degradation is calcium and calmodulin independent. A: Pnck-induced EGFR degradation is calcium independent. Human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells stably expressing Neo (lanes 1–3 and 7–9) or hemagglutinin (HA)-Pnck (lanes 4–6 and 10–12) were serum starved for 3 h and incubated with either vehicle (DMSO) (lanes 1–6) or 10 μM BAPTA-AM for 30 min (lanes 7–12), then stimulated without (lanes 1, 4, 7, and 10) or with (lanes 2, 5, 8, and 11) 10 nM EGF for 5 min (E) or with 10% heat-inactivated serum (lanes 3, 6, 9, and 12) for 10 min (F). B: Pnck-induced EGFR degradation is calmodulin independent. HEK-293 cells stably expressing Neo (lanes 1–3 and 7–9) or HA-Pnck (lanes 4–6 and 10–12) were serum starved for 3 h and incubated with either vehicle (DMSO) (lanes 1–6) or 30 μM W-7 (lanes 7–12) for 45 min, and then stimulated without (lanes 1, 4, 7, and 10) or with (lanes 2, 5, 8, and 11) 10 nM EGF for 5 min (E) or with 10% heat-inactivated serum (lanes 3, 6, 9, and 12) for 10 min (F). For both A and B, cells were lysed and equal amounts of total protein were immunoblotted for EGFR [Western blot (WB): EGFR], HA-Pnck (WB: HA-Pnck), phospho-MAPK (WB: P-MAPK), MAP kinase (WB: MAPK), and β-actin (WB: β-actin). A representative example of three independent experiments is presented.