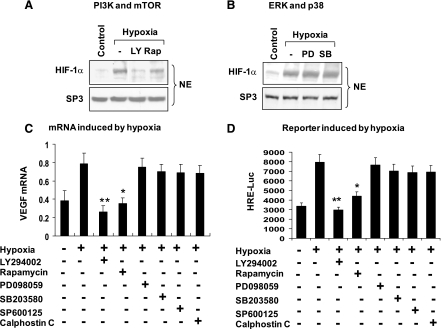
Fig. 5.
Signaling for HIF-1α elevation. A: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in the control of HIF-1α activity. Differentiated 3T3-L1 cells were serum starved and pretreated with LY-294002 (LY) and rapamycin (Rap) for 0.5 h and then treated with hypoxia for 8 h. The HIF-1α protein was examined in the nuclear extract in a Western blot. B: ERK and p38. The nuclear HIF-1α was determined in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells treated with PD-098059 (PD) or SB-203580 (SB) for 0.5 h. C: inhibition of HIF-1 function by kinase inhibitors. Differentiated 3T3-L1 cells were pretreated with kinase inhibitors such as LY (PI3K), Rap (mTOR), PD (MEK/ERK), SB (p38), SP-600125 (JNK), and calphostin C (PKC) for 0.5 h, followed by hypoxia treatment. VEGF mRNA was examined after hypoxia treatment for 8 h. D: HRE-luc assay. The HRE-luc reporter was transfected into 293 cells and induced with hypoxia after the inhibitor treatment for 0.5 h. The luciferase activity was measured after hypoxia treatment for 8 h. In the bar graph, each data point represents means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001 (n = 3). NE, nuclear extract.