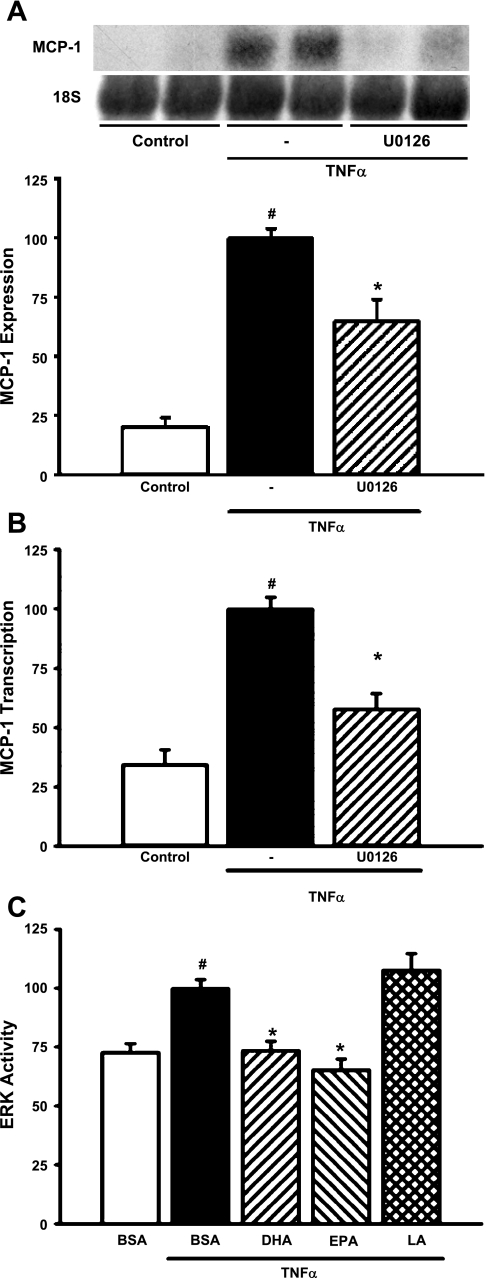
Fig. 2.
n-3 Fatty acids inhibit TNF-α-stimulated MCP-1 expression at least in part through suppression of ERK activity. A: U0126 blocks TNF-α-stimulated MCP-1 mRNA expression. MCs were pretreated with U0126 (25 μM) for 1 h before exposure to TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. Northern blots of total RNA were hybridized with a rat MCP-1 probe, and data were normalized to 18S rRNA. Values are expressed as means ± SE relative to TNF-α-treated cells; n = 4 experiments. #P < 0.05 vs. control. *P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α-treated cells. Inset: representative Northern blot. B: U0126 blocks TNF-α-stimulated transcription of the MCP-1 gene. MCs were cotransfected with MCP-1/pGL3 and a Renilla luciferase control plasmid (phRG-Basic) for 8 h and then pretreated with U0126 (25 μM) for 1 h and exposed to TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. Luciferase activity was assessed using the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega). Values are expressed as means ± SE relative to TNF-α-treated cells; n = 3 experiments. #P < 0.05 vs. control. *P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α-treated cells. C: n-3 fatty acids block TNF-α induction of ERK activity. ERK activity in MCs was assessed by a transfection-based in vivo kinase assay (Stratagene) as described in materials and methods. Transfected MCs were treated for 24 h with 20 μM DHA, EPA, or LA and exposed to TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. Luciferase activity was assessed using the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega). Values are expressed as means ± SE relative to TNF-α-treated cells; n = 4 experiments. #P < 0.05 vs. BSA control. *P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α-treated cells.