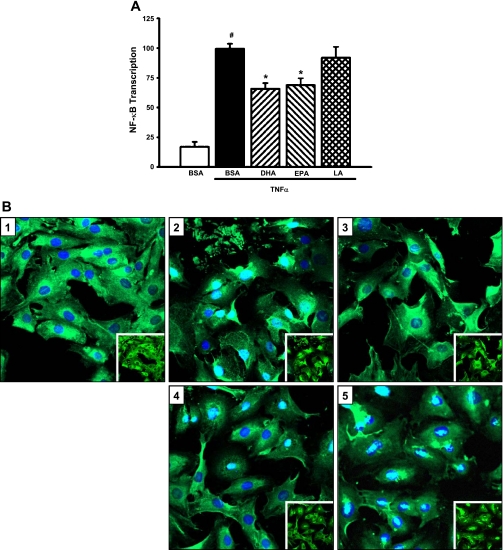
Fig. 4.
n-3 Fatty acids block TNF-α-induced NF-κB activity. A: n-3 fatty acids downregulate TNF-α-stimulated NF-κB transcription. MCs were cotransfected with NF-κB/pGL2 and a Renilla luciferase control plasmid (phRG-Basic) for 8 h, pretreated with fatty acids (20 μM) for 24 h, and stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 6 h. Luciferase activity was assessed using the Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega). Values are expressed as means ± SE relative to TNF-α-treated cells; n = 4 experiments. #P < 0.05 vs. BSA control. *P < 0.05 vs. TNF-α-treated cells. B: n-3 fatty acids decrease TNF-α-stimulated nuclear translocation of NF-κB. MCs were pretreated with fatty acids (20 μM) for 24 h and stimulated with TNF-α for 1 h. Cells were fixed and immunostained for the p65 subunit of NF-κB, and nuclei were stained with DAPI. Slides were analyzed by confocal microscopy. 1: BSA alone. 2: BSA + TNF-α. 3: DHA + TNF-α. 4: EPA + TNF-α. 5: LA + TNF-α. Insets: same images without DAPI stain overlay.