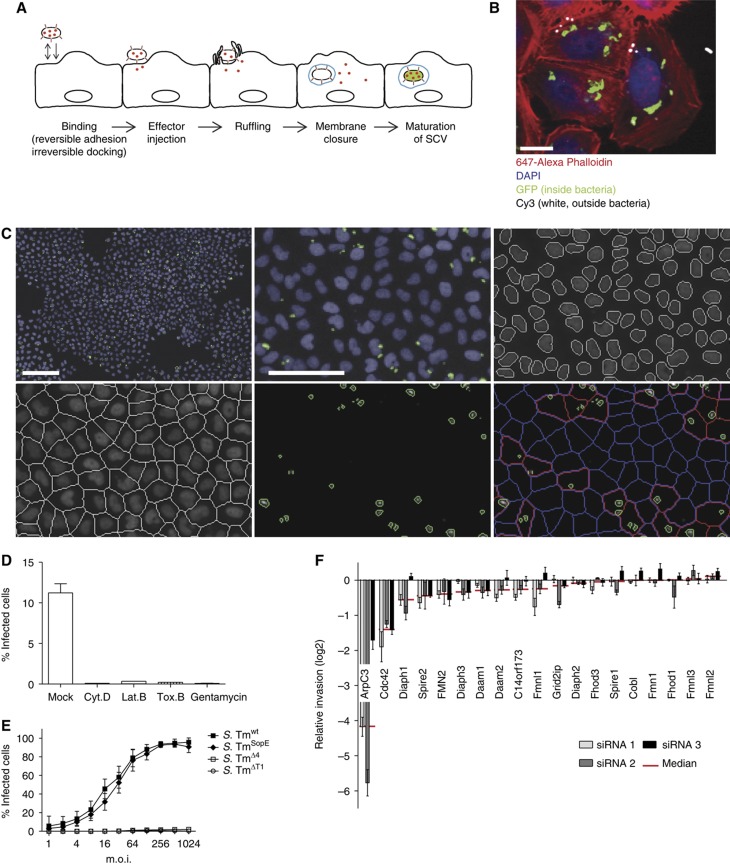
Figure 1.
Establishment of an automated assay to analyze S. Typhimurium invasion. (A) Overview showing the invasion process of S. Typhimurium divided into five major steps: (i) during the binding step, the bacteria attach to the cellular surface by reversible adhesion or irreversible docking; (ii) T1 is used as a molecular syringe to inject effectors (shown in red) into the eukaryotic cell; (iii) these effectors in turn induce membrane ruffling; (iv) subsequently the cellular membrane encloses a bacterium (membrane closure), thereby producing a Salmonella-containing vacuole (SCV, shown in blue); (v) after a maturation step, S. Tm genes important for intracellular survival are induced (green). (B) Fluorescence image showing GFP expression of S. Tmwt (pM975) only after invasion into HeLa cells (green=inside bacteria, red=actin, blue=DAPI, white=outside bacteria; scale bar=20 μm). (C) Automated image analysis strategy: S. Tmwt (pM975) infection of HeLa cells followed by the acquisition of nuclei (blue) and bacterial spots (green) using an automated microscope with a × 10 objective. Images were analyzed using CellProfiler as follows: recognition of nuclei, definition of cells, identification of bacterial spots and the allocation of these spots to cells (red outline=infected cell, blue outline=non-infected cell; scale bar whole image=100 μm, detailed image=50 μm). (D) Verification of the automated assay testing inhibitors of Salmonella invasion. HeLa cells were infected with S. Tmwt (pM975) and analyzed as described in (C). Pretreatment of HeLa cells with the inhibitors Cytochalasin D (Cyt. D), Latrunculin B (Lat. B), Toxin B (Tox. B) or the antibiotic gentamycin prevents invasion. (E) Invasion efficiencies of various Salmonella strains into HeLa cells analyzed by the automated assay showing S. TmSopE (pM975) invasion being as efficient as S. Tmwt (pM975). (F) Verification of the automated assay using siRNAs directed against different actin polymerization regulators. Depletion of ArpC3 and Cdc42 reduces S. TmSopE (pM975) invasion (red line=median of three siRNAs tested for each gene; log2 relative invasion=% infected cells with siRNA treatment divided by the median of % infected cells treated with control siRNA).