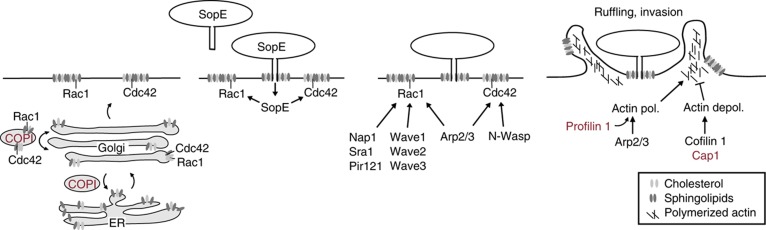
Figure 8.
Model for S. Typhimurium entry into HeLa cells. In order to invade, S. Typhimurium binds onto cells and injects a cocktail of effectors. This study investigates the action of the key effector SopE. SopE mediates the GTP nucleotide exchange and thereby the activation of the Rho GTPases Rac1 and Cdc42. This leads to the activation of the Arp2/3 complex, actin polymerization cellular ruffling and bacterial entry. The screen identified key regulators of this process, including Nap1, Cdc42, Profilin 1 and the Arp2/3 complex, as well as proteins mediating actin depolymerization, a process probably counteracting the activity of Rac1 and Cdc42. The correct localization seems to be as important as the activation of the Rho GTPases. Upon depletion of the COPI complex, cholesterol and Rho GTPases are mislocalized away from the cell membrane, leading to a much less efficient S. Typhimurium entry. Proteins newly identified to be implicated in S. Typhimurium entry are indicated in red. Proteins that have already been described to have a role in the infection and were found in the screen are indicated in black.