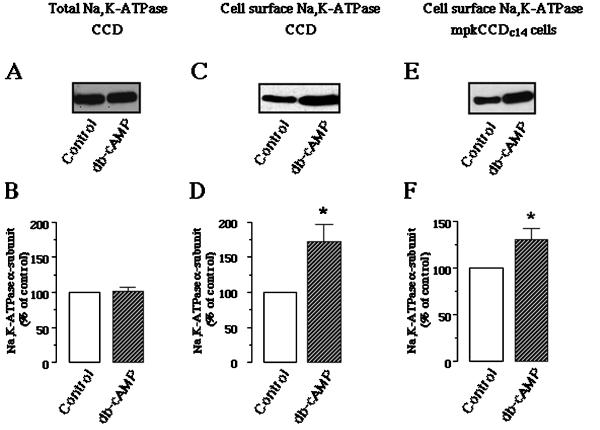
Figure 3.
Effect of db-cAMP on total and cell surface amount of Na,K-ATPase in rat CCDs and in mpkCCDc14 cells. (A and B) Total amount of Na,K-ATPase in control and db-cAMP treated rat CCDs. Same amounts of microdissected rat CCDs were incubated in the absence or presence of 10−3 M db-cAMP for 15 min at 37°C. CCDs were then lysed and the Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting using a specific polyclonal antibody. (A) Representative immunoblot. (B) Bars represent the densitometric quantification (means ± SE) from four different experiments. Results are expressed as percentage of the optical density values from untreated samples (control). (C–F) Cell surface amount of Na,K-ATPase in control and db-cAMP-treated rat CCDs and mpkCCDc14 cells. Microdissected rat CCDs or mpkCCDc14 cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 10−3 M db-cAMP for 15 min (CCDs) or 30 min (mpkCCDc14) at 37°C. After biotinyla-tion, samples were lysed and labeled proteins were precipitated by streptavidin-agarose beads. The Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting using a specific polyclonal antibody. (C and E) Representative immunoblots. (D and F) Bars represent the densitometric quantification (means ± SE) from 12 independent experiments. Results are expressed as percentage of the optical density values from untreated samples (control); ∗, p < 0.05 versus control values.