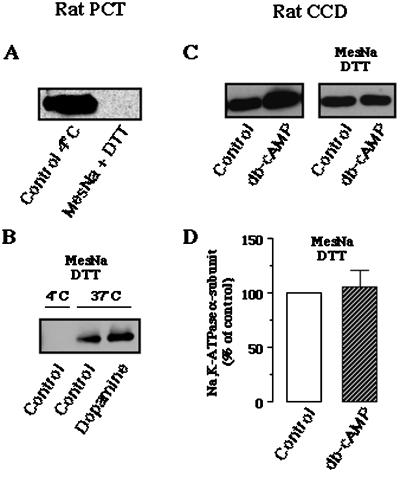
Figure 5.
Internalization of Na,K-ATPase: effect of db-cAMP in rat CCDs. (A and B) Validation of the biotinylation/debiotinylation procedure on rat PCT suspensions. (A) Rat PCTs were first biotinylated and then either maintained at 4°C or immediately washed four times at 4°C in reducing buffer (Mes-Na, DTT) to allow debiotinylation of cell surface proteins. After cell lysis and streptavidin agarose-beads precipitation, the Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting as described in Figure 3. (B) After biotinylation, rat PCTs were debiotinylated at 4°C by the Mes-Na-DTT buffer either immediately or after incubation for 30 min at 37°C in the absence or presence of 10−6 M dopamine. After cell lysis, labeled proteins were precipitated by streptavidin agarose-beads, and Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting as described in Figure 3. (C and D) Effect of db-cAMP on the internalization of Na,K-ATPase in rat CCDs. (C, left) Microdissected rat CCDs were incubated without or with 10−3 M db-cAMP for 15 min at 37°C. After biotinylation, CCDs were lysed, labeled proteins were precipitated by streptavidin-agarose beads, and Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting. (C, right) Microdissected rat CCDs were biotinylated and incubated in absence or presence of 10−3 M db-cAMP for 15 min at 37°C. Tubules were then debiotinylated by washes at with 4°C Mes-Na-DTT buffer, lysed, and labeled proteins were precipitated by streptavidin agarose-beads and the Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was analyzed by Western blotting. (D) Bars represent the densitometric quantification (means ± SE) from nine experiments such as those shown in C (right). Results are expressed as percentage of the optical density values from untreated samples (control).