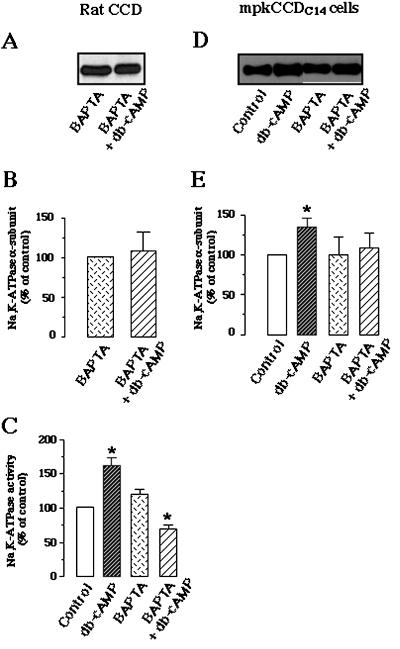
Figure 8.
db-cAMP–induced cell surface expression and stimulation of Na, K-ATPase were dependent on intracellular Ca2+. Microdissected rat CCDs or mpkCCDc14 cells were preincubated without or with 10 μM BAPTA-AM at room temperature (CCDs) or at 37°C (mpkCCDc14 cells) for 1 h, and then incubated C (15 min for CCDs and 30 min for mpkCCDc14 cells) in the absence or presence of 10−3 M db-cAMP at 37°. Samples were then biotinylated, lysed, and labeled proteins were precipitated by streptavidin agarose-beads. The Na,K-ATPase α-subunit was detected by Western blotting as described in Figure 3. (A and D) Representative immunoblots from CCD (A) and mpkCCDC14 cells (D), respectively. (B and E) Bars represent the densitometric quantification (means ± SE) from three and four independent experiments in rat CCDs and mpkCCDc14 cells, respectively. Results (means ± SE) are expressed as percentage of the optical density values from untreated samples (control); ∗, p < 0.05 versus control values. (C) Hydrolytic activity of Na,K-ATPase in rat CCDs treated with BAPTA-AM and db-cAMP as described above. Values (means ± SE from 7 independent experiments) are percentage of control (370 ± 53 pmol ATP · mm−1 · h−1). ∗, p < 0.05 versus control values.