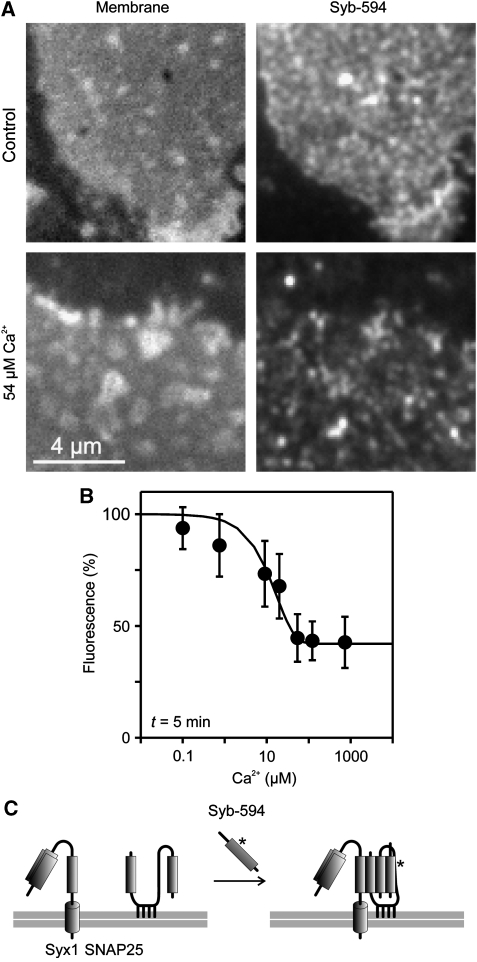
Figure 6.
Ca2+ inhibits SNARE reactivity. (A, B) Freshly prepared membrane sheets were incubated for 5 min with 10 μM Alexa594-labelled soluble synaptobrevin 2 in the presence of variable Ca2+ concentrations, washed, fixed and binding of synaptobrevin to membrane sheets was quantified by fluorescence microscopy. (A) (Left) TMA-DPH phospholipid staining visualizing the basal plasma membrane; (right) membrane-bound synaptobrevin. (B) For each Ca2+ concentration incorporated synaptobrevin was quantified and intensity was related to the value obtained in the absence of Ca2+ (set to 100%). Values are given as means±s.e.m. (n=4–5 experiments, 12–66 membrane sheets were analysed for one condition in one experiment). (C) Illustration of the biochemical reaction underlying synaptobrevin 2 binding to the plasma membrane. Synaptobrevin binding depends on both syntaxin 1 and SNAP25 (Lang et al, 2002), which form an acceptor complex (not shown for clarity) that in turn interacts with soluble synaptobrevin, resulting in a so-called cis-SNARE complex (right).