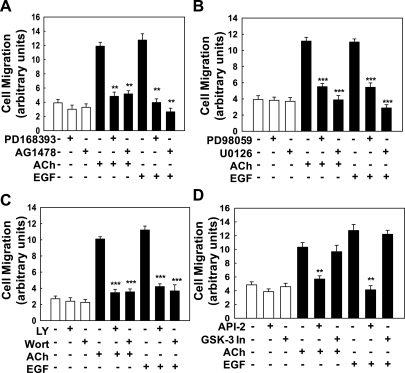
Fig. 2.
ACh-induced colon cancer cell migration is dependent on ERBB1 activation and post-ERBB1 signaling. Human colon cancer cells were plated at confluence before a linear wound was made. As described in materials and methods, photomicrographs were taken immediately after a linear wound was made and again 8 h after addition of test agents. A: ACh (100 μM)- and EGF (10 μg/ml)-induced migration of H508 colon cancer cells was attenuated by adding ERBB1 activation inhibitors (PD168393, AG1478; both 10 μM). B: ACh (100 μM)- and EGF (10 μg/ml)-induced migration of H508 colon cancer cells was attenuated by adding ERK activation inhibitors (PD98059 and U0126; both 10 μM). C: ACh (100 μM)- and EGF (10 μg/ml)-induced migration of H508 colon cancer cells was attenuated by adding phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activation inhibitors [10 μM LY294002 (LY) and 50 nM wortmannin (Wort)]. D: ACh (100 μM)- and EGF (10 μg/ml)-induced migration of H508 colon cancer cells was attenuated by adding an inhibitor of AKT activation (5 μM API-2) but not by adding a GSK-3 inhibitor (50 nM GSK-3 inhibitor IX). Values are means ± SE from at least 3 separate experiments. **, ***P < 0.01 and 0.001, respectively, compared with control (treatment with vehicle alone).