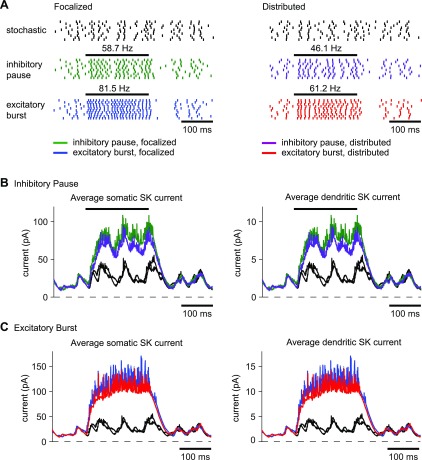
Fig. 9.
Response to an inhibitory input pause or excitatory input burst for focalized or distributed input in the model. A: a 50% decrease in the inhibitory input rate approximately doubled the output spike rate of the model. This increase was slightly higher for focalized inputs, which is likely due to greater excitation on the soma in the focalized case. A 100% increase in the excitatory input rate had an effect similar to that of an inhibitory pause but drove the model to spike at even higher frequencies. B: during the inhibitory pause, the magnitude of the SK was larger due to increased spiking. C: the effect of an excitatory burst was similar to that of an inhibitory pause with the magnitude of the SK current driven even higher by the higher spike rate. The effect for both input conditions was somewhat stronger for focalized than for distributed inputs due to the higher achieved spike rate. In all cases, the SK current took about 60 ms to relax back to the control trajectory after the end of the input burst.