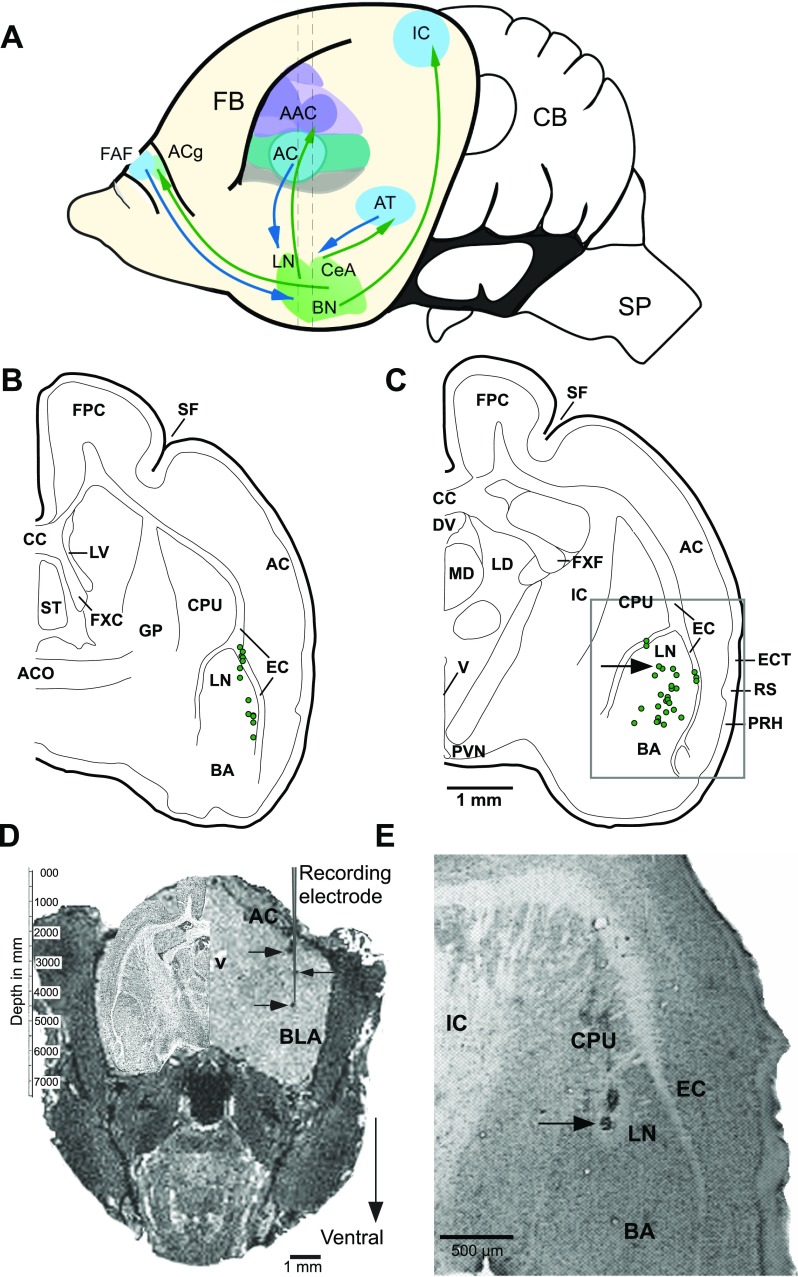
Fig. 1.
A. An outline of the mustached bat brain illustrating reciprocal connections between the amygdala and structures in the auditory forebrain of mammals (Armony et al. 1997; LeDoux et al. 1990a,b). Basolateral amygdala (BLA) also receives projections from the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (McDonald et al. 1996) where a frontal auditory field (FAF) is present in this species. Central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) projects back to the anterior cingulate (ACg) (Ghashghaei and Barbas 2002), and basal nuclei (BN) projects to the inferior colliculus (IC) within the brainstem (Marsh et al. 2002). Vertical dashed lines indicate the antero-posterior levels of the sections charted in B and C, respectively. B and C: reconstruction of locations of 55 recorded units from 48 different sites in the basolateral complex of the amygdala. Units recorded from the left (12) and right (43) hemispheres at each rostrocaudal level are plotted on the same hemisection. Two sections are separated by ∼600 μm along the rostrocaudal axis. Recording sites were located within 300 μm of the section plane. Grey rectangular outline in C shows location of the image in E. D: digitally sectioned coronal image of a bat brain with dark spots (on right side) indicating iron deposited in an electrode track and visualized using MRI procedure (grey vertical line representing a recording electrode is superimposed to emphasize collinearity of deposits). Iron deposits were made at depths of 1.5, 3.0, and 3.75 mm from the skull surface with anodal current levels of 2, 2, and 3 μA, respectively. Current duration ranged from 15 to 20 s. A high contrast Nissl-stained section from equivalent anteroposterior level of the brain is superimposed in the cranial space on the left. See text for imaging parameters. Recordings were subsequently performed in this animal. E. photomicrograph of a Nissl-stained coronal section showing a lesion mark at one of the recording sites. Arrow in D indicates the position of the recovered lesion indicated in C, projected caudally onto the schematic. AC, anterior cortex; AAC, auditory association cortex; ACO, anterior commissure; AT, auditory thalamus; BA, basal nucleus of the amygdala; CB, cerebellum; CPU, caudate putamen; CC, corpus callosum; DV, dorsal third ventricle; EC, external capsule; ECT, ectorhinal cortex; FB, forebrain; FPC, frontoparietal cortex; FXC, column of the fornix; FXF, fimbria of the fornix; GP, globus pallidus; LD, lateral dorsal nucleus of the thalamus; LN, lateral nucleus; LV, lateral ventricle; MD, mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus; PRH, perirhinal cortex; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; RS, rhinal sulcus; SF, sylvian fossa; SP, spinal cord; ST, septal triangular nucleus; V, ventricle.