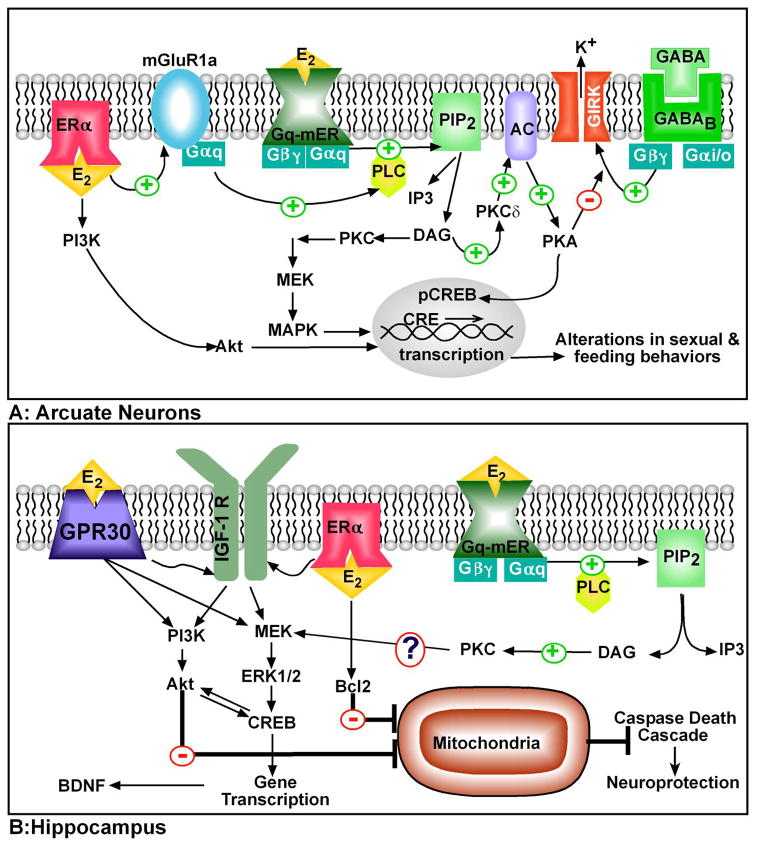
Figure 1. Cellular models of membrane-initiated E2 signaling pathways in the brain.
A. In arcuate neurons including those that express POMC, dopamine, and GABA, E2 activates the Gq-mER leading to activation of PLC-PKC-PKA pathway. Activation of the receptor initiates the hydrolysis of membrane-bound phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate (PIP2) to IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG) via PLC. DAG activates protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ), which through phosphorylation, upregulates adenylyl cyclase VII (AC) activity. The generation of cAMP activates PKA, which can rapidly uncouple GABAB receptors from their effector system through phosphorylation of a downstream effector molecule (e.g., G protein-coupled, inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channel). The mER-mediated modulation of kinase pathways reduces the capacity of inhibitory neuromodulators such as GABA via GABAB receptor (and opioid peptides via mu-opioid receptor, not shown) to reduce neuronal excitability. The Gq-mER-mediated activation of PKA can lead to phosphorylation of cAMP-responsive element binding protein (pCREB), which can then alter gene transcription through its interaction with CREs on genes. Also, in arcuate (NPY?) neurons, ERalpha interacts with metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a (mGluR1a) to initiate Gq stimulation of PLC, which leads to MAPK-induced CREB phosphorylation. Membrane-associated ERalpha can activate PI3K/Akt signaling. B: Membrane-initiated E2 signaling treatment may act through multiple cellular pathways for its neuroprotective actions. Acute E2 administration may bind to either classical membrane ERs (ERalpha is shown) and/or GPR30. Through the membrane-associated ERs, E2 can either directly control Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic protein) gene expression or by transactivation of IGF-1 receptors for a sustained activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. GPR30 may block apoptotic cascades through the direct activation of either ERK/MAPK or PI3K/Akt pathways via the transactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases (IGF-1 receptors and/or Trk-B). BDNF, a target of activated CREB, is thought to bind the receptor tyrosine kinase Trk-B to activate both the MAPK and PI3K pathway to promote neuroprotection. Stimulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by BDNF would inactivate the pro-apoptotic proteins to halt the caspase death cascade. STX treatment also offers neuroprotection from ischemia via an unknown mechanism, but a possible pathway is the PKC-activation of MAPK signaling.