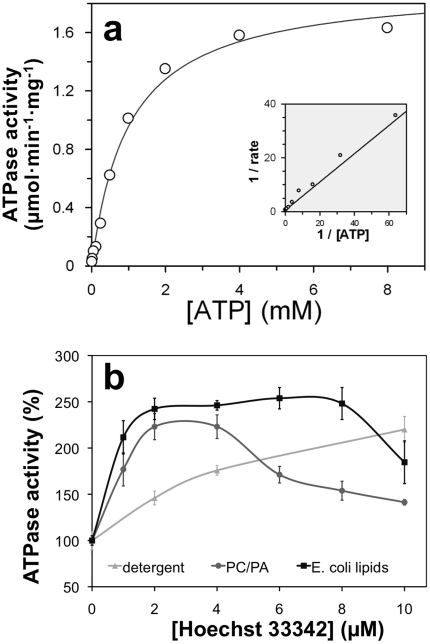
Figure 4. Reconstitution of BmrC/BmrD into proteoliposomes.
BmrC/BmrD were reconstituted at lipid to protein ratio of 40 (w/w) by detergent removal from different solubilized mixtures of DDM/lipid/protein. (a) ATPase activity of proteoliposomes was assessed at 4 mM ATP. E. coli: total extract of E. coli phospholipids; PC: egg-phosphatidylcholine; PA: egg-phosphatidic acid; chol: cholesterol; DOPC: dioleoylphosphatidylcholine; DOPG: dioleoylphosphatidylglycerol; CL: cardiolipin. Lipid composition was as follows (w/w): PC/PA 9∶1; PC/PA/chol 7∶1∶2; DOPC/DOPG 9∶1; PC/CL 8∶2. (b) Cryo-electron microscopy of reconstituted proteoliposomes with EPC/EPA. All proteoliposomes were unilamellar and showed a continuous lipid bilayer. Scale bar: 50 nm. (c) ATPase activity measured after reconstitution of BmrC/BmrD with EPC/EPA or E. coli lipids at lipid to protein ratio of 40 (w/w) and 100 (w/w). (d) Protein incorporation in proteoliposomes after fractionation in a sucrose gradient. The amount of BmrC/BmrD in every fraction was measured by quantitation of the protein bands revealed by immunoblot (the intensity of both bands were added) and normalization to the total amount of BmrC/BmrD loaded onto the sucrose gradient (cf. Materials and Methods). Most proteins were reconstituted in proteoliposomes running at 2.5%–5% sucrose without significant aggregates at 30% sucrose.