Figure 1. Endothelium-dependent, nitric oxide-dependent and endothelium-independent dilation.
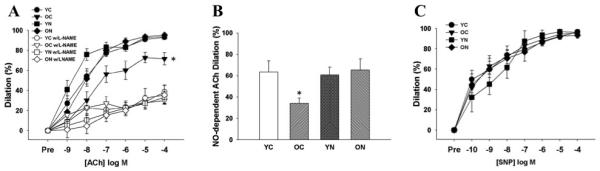
(A) Dose-responses to the endothelium-dependent dilator acetylcholine (ACh) in the absence and presence of the endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N-G-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) in young and old control (YC and OC) and nitrite-supplemented (YN and ON) mice. (B) NO-dependent dilation (Max DilationACh – Max DilationACh+L-NAME). (C) Dose-responses to the endothelium-independent dilator sodium nitroprusside (SNP). Values are mean ± SEM. (n = 7 per group). * p < 0.05 vs. YC.
