Figure 2. Superoxide-, NADPH oxidase- and tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent modulation of endothelial-dependent dilation.
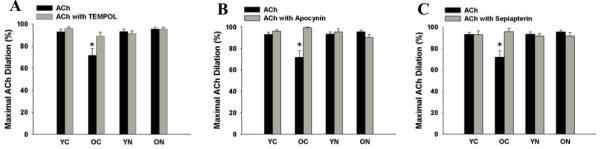
(A) Maximal dilation of carotid arteries to acetylcholine (ACh) and ACh + TEMPOL, a superoxide dismutase mimetic. (B) Maximal dilation of carotid arteries to ACh and to ACh + apocynin, a NADPH oxidase inhibitor. (C) Maximal dilation of carotid arteries to ACh and to ACh + sepiapterin, an exogenous tetrahydrobiopterin donor. Values are mean ± SEM. (n = 6 – 9 per group) * p < 0.05 vs. YC.
