Figure 4.
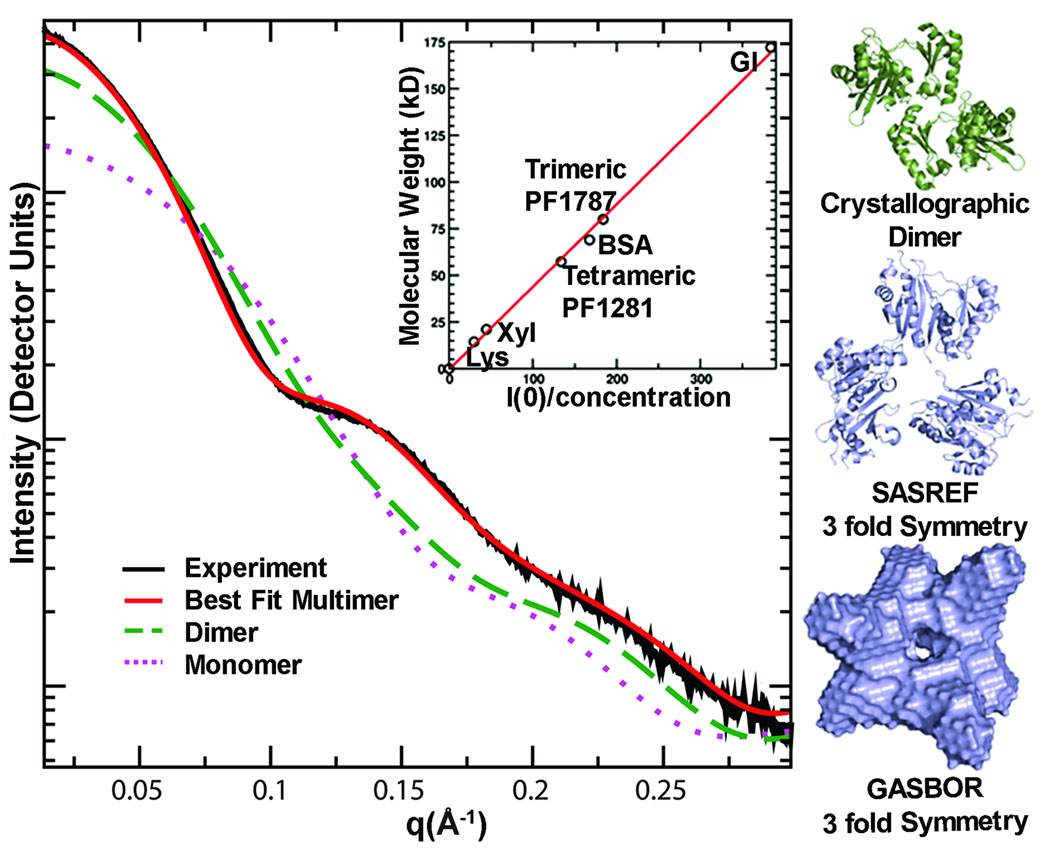
SAXS determines accurate assembly state in solution, as shown for acetyl-CoA synthetase subunit (PF1787). The experimental scattering curve for PF1787 (black) is shown with calculated scattering curves for monomeric (magenta dots) and dimeric (green dashes) atomic resolution structures of homologs. The best fit (red) to the experimental SAXS data is calculated from a 3-fold symmetric trimer derived from a monomeric homologue (PDB 1WR2). The trimeric form of PF1787 was confirmed using I(0), the extrapolated intensity at 0 scattering angle, normalized for concentration (inset). Proteins standards lysozyme (Lys), xylanase (Xyl), PF1281, bovine serum albumin (BSA) and glucose isomerase (GI) were used to place the data on a relative scale. Relevant structures from analysis of PF1787 are shown on the right. The crystallographic dimer (green) is a flexibly-linked 2-domain protein. Models with 3-fold symmetry enforced (blue) match the SAXS results.