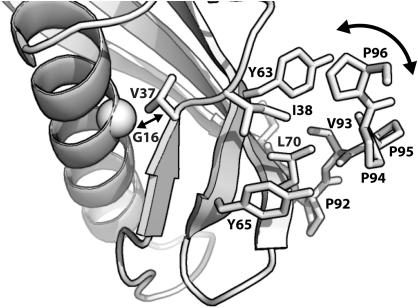
Figure 4.
Model for disruption of the C-terminal PPII helix by G16A mutation. Mutation of G16 to alanine causes a minor reorientation of the adjacent V37 residue (straight double arrow) that is propagated, via changes to the intermediate network of hydrophobic interactions (labeled residues shown as sticks), to increase protein flexibility and disrupt the C-terminal PPII helix structure formed by P94–P96.