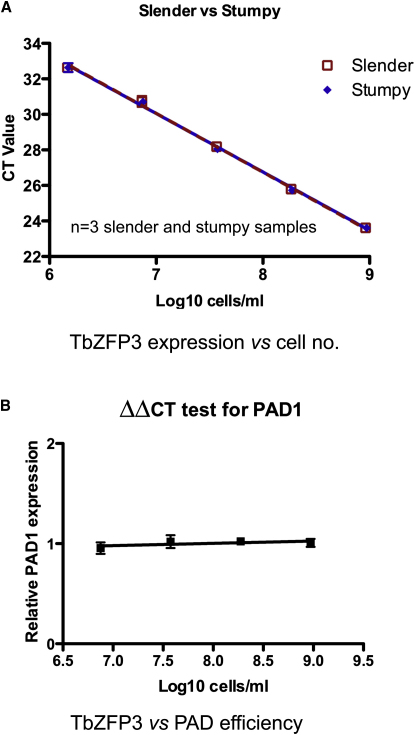
Figure 1.
Validation of qRT-PCR Method
(A) Validation of the constitutive expression of TbZFP3 mRNA. TbZFP3 specific primers were used to amplify cDNA derived from serial dilutions of samples that were derived from populations that were either slender or stumpy in morphology (these having been derived from mouse infections). Triplicate assays are shown, which demonstrated that neither the slope nor the intercept of the regression lines of TbZFP3 expression in the slender and stumpy samples were significantly different (F1,25 = 0.048, p = 0.8276; and F1,26 = 0.004, p = 0.9493) over a 1000-fold range (1.5 × 106 to 9 × 108 trypanosomes/ml), with a combined PCR efficiency of 100.92%. This established that the level of mRNA for TbZFP3 was equivalent in each cell type.
(B) The efficiency of amplification of amplicons detecting either TbZFP3 or PAD1 was compared over serial dilutions of stumpy forms (7.3 × 106 to 9 × 108 trypanosomes/ml). Equivalent amplification efficiency was observed for each target transcript, there being a semi-log regression line of slope 0.023. Error bars representing standard error of the mean (SEM) are included for the triplicate assays, these being difficult to visualize on the derived plots due to the high level of reproducibility of the assays.