Figure 5.
Fz and Stbm Stabilize Junctional Fmi
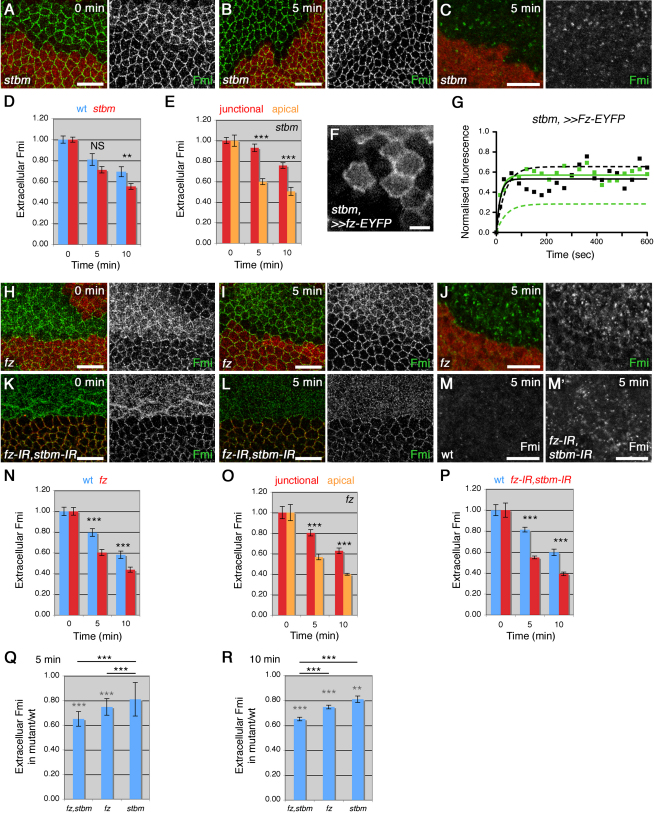
Fmi antibody internalization (A–E and H–R) or Fz-EYFP FRAP (F and G) in mutant backgrounds. (A–C and H –M) Images of Fmi antibody internalization in stbm6 clones (A–C), fzP21 clones (H–J), and ptc-GAL4, UAS-fz-IR,UAS-stbm-IR (K–M), mutant tissue marked by loss of β-gal (red, A–C and H –J) or loss of Stbm (red, K and L). (A, H, and K) Extracellular Fmi (green) with 0-min chase. (B, I, and L) Extracellular Fmi (green) with 5-min chase. (C, J, and M) Total Fmi staining with 5-min chase, subapical sections. (M) and (M′) show Fmi staining in wild-type and fz,stbm mutant regions of the same wing. Steady-state levels of Fmi are increased in mutant tissue (1.8-, 2.2-, and 2.0-fold for stbm, fz, and the double mutant, respectively). Scale bars, 10 μm. (D, E, and N–R) Quantitation of extracellular staining. (D, N, and P) Total extracellular staining, asterisks indicate p values of mutant relative to wild-type at the same time point. Because absolute internalization varied significantly between experiments (Figure S1A), mutant and wild-type tissue within the same wings was compared. (E and O) Junctional or apical extracellular populations of Fmi. Asterisks indicate p values comparing junctional and apical Fmi. (Q nd R) Relative internalization of Fmi in mutant relative to wild-type tissue, at 5- and 10-min chase times. Gray asterisks indicate p values relative to wild-type at the same time point; black asterisks indicate p values comparing genotypes as indicated by the bar. Image (F) or FRAP analysis (G) on live wings of genotype Ubx-FLP; ActP-FRT-polyA-FRT-fz-EYFP, stbm6/stbm6. (F) Scale bar 5 μm. (G) FRAP on bright (green) or less-bright (black) regions; dotted lines indicate 28-hr wing data for Ubx-FLP; ActP-FRT-polyA-FRT-fz-EYFP/+ for comparison (see Figure 4H). See also Figures S1–S3.