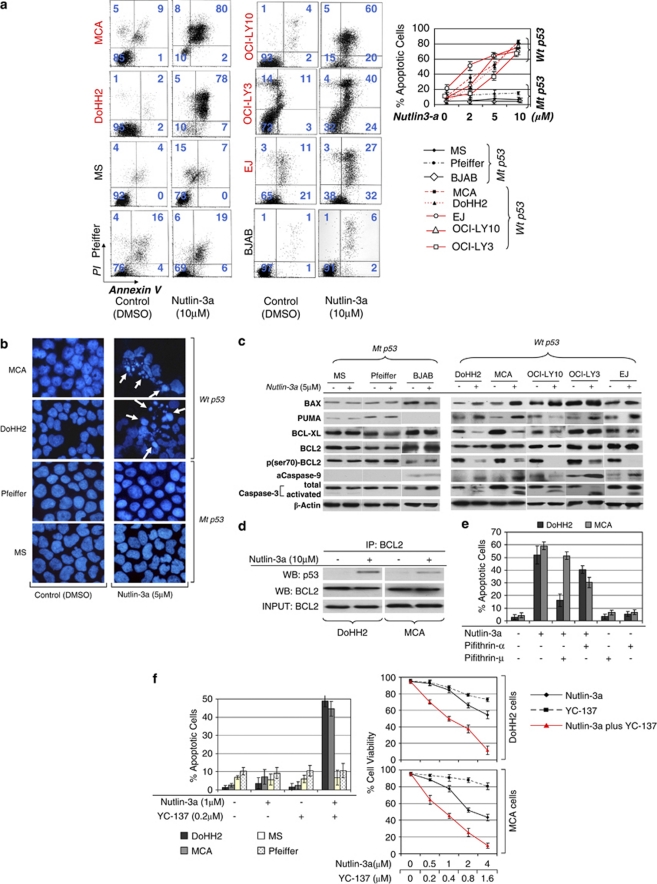
Figure 3.
Nutlin-3a induces apoptotic cell death of t(14;18)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and ABC-type DLBCL cells through activation of the p53 pathway. (a) At 48 h after incubation with 10 μ nutlin-3a, a considerable increase in annexin V binding was observed in DLBCL cells with wild-type (wt) p53, indicating apoptotic cell death. No significant change was observed in Pfeiffer, BJAB and MS cells, which have mutant p53 (left panel). Annexin V binding corresponding to various concentrations of nutlin-3a treatment is depicted in the diagrams of the right panel (b). Microscopic examination of 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-stained preparations of DoHH2 and MCA cell at 48 h after treatment with 5 μ nutlin-3a showed morphologic evidence of apoptosis, including nuclear condensation and fragmentation, whereas no such changes were observed in nutlin-3a-treated Pfeiffer and MS cells. (c) Western blot analysis of DLBCL cells with wt p53 after treatment with nutlin-3a showed increased levels of the proapoptotic proteins BAX and PUMA in all cell lines with wt p53, known transcriptional targets of p53. Also, substantially decreased levels of BCL-XL levels were observed after nutlin-3a treatment in DoHH2, OCI-LY10 and MCA cells, without much change in OCI-LY3 and EJ cells. Whereas the levels of total BCL2 remained constant, the p-Ser70BCL2 levels decreased dramatically after nutlin-3a treatment in all the cells with wt p53. In addition, western blot analysis demonstrated cleavage of caspase-3, accompanied by activation of caspase-9. By contrast, no significant changes in the levels of proapoptotic or antiapoptotic proteins, or in activation of caspase-3 or -9, were observed in nutlin-3a-treated Pfeiffer and MS cells. Lysates were prepared at 24 h following nutlin-3a treatment. (d) Coimmunoprecepitation of DoHH2 and MCA cell lysates treated with 10 μ of nutlin-3a or control (dimethyl sulfoxide) showed that nutlin-3a induced binding of BCL2 by p53 protein, suggesting that non-transcriptional mechanisms are also involved in nutlin-3a-induced cell death of t(14;18)-positive DLBCL cells. (e) Preincubation of DoHH2 and MCA cells with 25 μ pifithrin-α (PFT-α) or 4.8 μ PFT-μ (the maximum non-toxic dose) rescued a substantial number of nutlin-3a-treated cells from apoptotic cell death. PFT-μ, an agent that inhibits the interaction of p53 with antiapoptotic proteins without affecting p53 transactivation function, rescued a greater proportion of nutlin-3a-treated DoHH2 cells and a smaller proportion of MCA cells, whereas PFT-α rescued a larger proportion of nutlin-3a-treated-MCA cells and a smaller proportion of DoHH2 cells. (f) Treatment with a comparatively small dose of nutlin-3a (1 μ) enhanced dramatically the cytotoxicity of YC-137, a BH3 mimetic in DoHH2 and MCA cells, with no effect observed in Pfeiffer and MS cells. Combined treatment with nutlin-3a and YC-137 synergistically induced decreased viability of DoHH2 and MCA cells (average combination index (CI)=0.53 and CI=0.35, respectively).