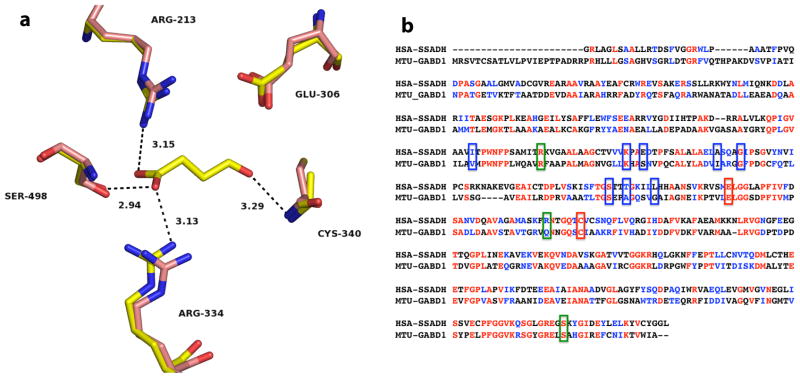
Fig. 1.
Active site of the human SSADH and primary sequence comparison with GabD1. (a) Active site of Cys340Ala mutant of human SSADH (yellow) in complex with SSA (PDB_ID 2W8Q), and the reduced form of the wild-type enzyme (pink) without SSA (PDB_ID 2W8O), at 2.4 Å and 3.4 Å resolution, respectively. Potential hydrogen bonds of SSADH with SSA are shown as dashed lines, with corresponding distances in Å. Image was generated using PyMol. (b) Alignment of human SSADH and M. tuberculosis GabD1. Amino acids highlighted in red are identical in both enzymes (31.5% identity) and amino acids highlighted in blue are strongly similar (20% strong similarity). Green boxes indicated residues involved in NAD+ binding, blue boxes indicate residues involved in SSA binding, and red boxes indicate residues that are involved in catalysis (Cys319 and Glu285, GabD1 numbering). Alignment was performed using ClustalW, with Blosum matrix, and the default parameters.