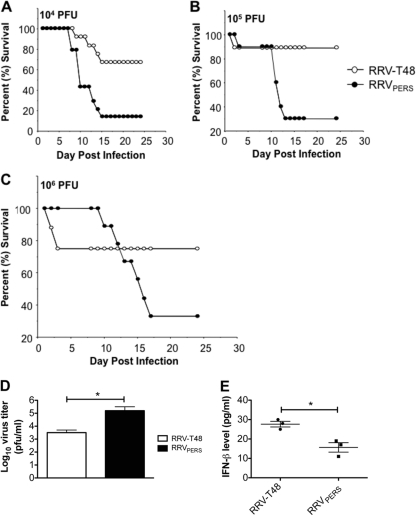
Fig. 5.
RRVPERS infection in mice results in enhanced mortality associated with reduced IFN-β expression. (A to C) Survival of 14-day-old Swiss outbred mice after intraperitoneal (i.p.) infection with RRV-T48 (open circles) or RRVPERS (closed circles). Virus was inoculated at doses ranging from 104 (A) or 105 (B) to 106 (C) PFU/mouse (n = 10). Differences between survival curves were calculated using the log rank test. P < 0.05 was considered to be significant. (D) Titers of RRV-T48 and RRVPERS (log10 PFU/ml) in the serum of 14-day-old Swiss outbred mice infected subcutaneously (s.c.) 24 h previously with 104 PFU/mouse. The plaque assay limit of detection is 2.0 log10 PFU/ml. Significant differences in virus titers (P < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk. (E) IFN-β concentration in homogenized lymph nodes of 5-week-old Swiss outbred mice 24 h after s.c. infection with 104 PFU RRV-T48 or RRVPERS (n = 3 mice per group). Significant differences in protein levels (P < 0.05) are marked with an asterisk.