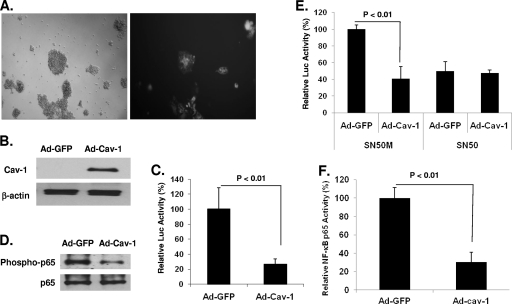
Fig. 7.
Cav-1 modulates HIV gene expression in primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. (A and B) Primary CD4+ T lymphocytes were isolated from human peripheral blood. Cells were dually infected with VSV-G-pseudotyped NL4-3.Luc.R−E− and adenovirus vector expressing GFP (Ad-GFP) or Cav-1 (Ad-Cav-1). The expression levels of GFP and Cav-1 are shown. (C) The levels of viral gene expression in the presence and absence of Cav-1 were measured by luciferase activity and determined relative to the levels in cells transduced with Ad-GFP. (D) p65 phosphorylation in the presence or absence of Cav-1 was evaluated by Western blot analysis. (E) The effect of Cav-1 on viral gene expression was measured in the presence of peptide SN50, an inhibitor of NF-κB cytoplasm-to-nucleus translocation, or the mutant SN50M. (F) Viral gene expression was measured by luciferase activity in one round of replication. NF-κB binding to target DNA in the presence and absence of Cav-1 was determined using an ELISA-based kit. All experiments were performed in triplicates, and results shown are means ± SD with P values.