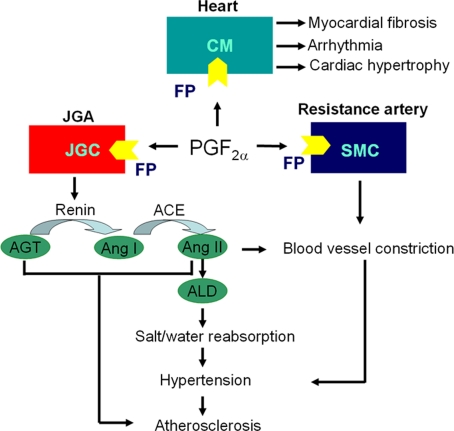
Figure 2.
Scheme of PGF2α/FP pathway involved in pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Cardiac fibroblasts derived PGF2α induces cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis and arrhythmia through FP receptor in adjacent cardiomyocytes (CMs); PGF2α stimulates renin release from juxtaglomerular granular cells (JGCs) by FP receptor in an autocrine fashion, and activate renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) to elevate blood pressure through enhancing salt/water reabsorption in kidney and constricting blood vessels directly via Angiotensin II (Ang II); PGF2α promotes resistance artery constriction through FP in smooth muscle cells (SMCs), which eventually increases blood pressure and contributes to atherosclerosis; Activated RAAS also accelerates atherosclerosis. JGA, juxtaglomerular apparatus; AGT, angiotensinogen; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ALD, aldosterone.