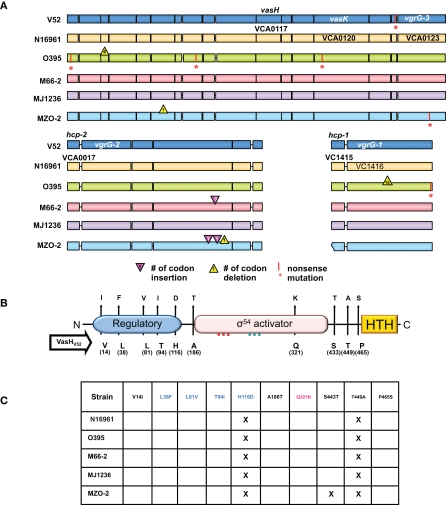
Figure 2.
T6SS clusters in V. cholerae strains with sequenced genomes. (A) Genomic alignments. Nucleotide sequences used for this study were obtained from Broad Institute and NCBI databases and compared with the blastn program from the stand-alone NCBI BLAST application (version 2.2.21). In-house Perl scripts were written to parse BLAST output and to compare genomic sequences of gene models for variations. BioPerl (http://www.bioperl.org/) modules were used. Regions containing the T6SS clusters of various V. cholerae strains (names on the left) were aligned. Each gene is indicated by a box in a color distinct for a particular strain. A vertical bar and an asterisk indicate the 3′-end of a truncated gene. Codon insertions are indicated by red triangles, while deletions are indicated by yellow triangles with numbers that indicate the insertion/deletion size (number of codons). Rough ends of a gene indicate that the complete sequence was not available. (B) Polymorphic domains of VasH. Graphical depiction of VasH from the O37 serogroup strain V52 (V52_VasH) with its putative N-terminal regulatory domain (blue), core sigma-54 activator domain (pink), and C-terminal helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain (yellow) (drawn to scale). Conserved amino acid substitutions are indicated by arrows. The residue and its position in VasH of V52 is indicated below the line and the substitutions found in other strains are indicated above the arrowhead. (C) Allelelic VasH variants. Listed are VasH variants of different V. cholerae strains compared to VasH in V52. Amino acid substitutions are listed for each variant. Font color indicates in which of the three domains the substitution is located.