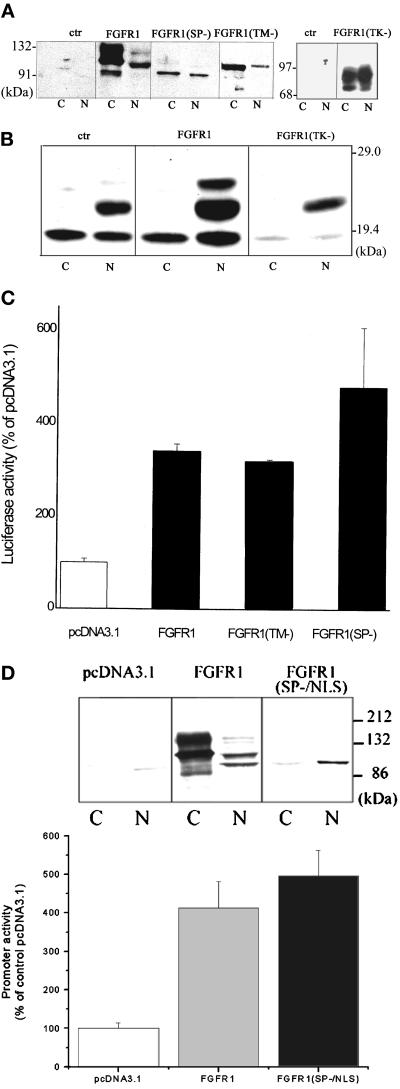
Figure 4.
Induction of intracellular FGFR1 is sufficient to transactivate the FGF-2 gene promoter. (A) TE671 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1FGFR1, pcDNA3.1FGFR1(TK−), pcDNA3.1FGFR1(TM−), pcDNAFGFR1(SP−), or with control pcDNA3.1. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions (30 μg of protein per lane) were purified 48 h later and were analyzed with FGFR1 McAb6. (B) TE671 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1FGFR1, pcDNA3.1FGFR1(TK−), or control pcDNA3.1 (1 μg each). Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) extracts were prepared 48 h later and analyzed by Western blot with polyclonal FGF-2 Ab. (C) (−650/+314)FGF-2Luc (1 μg) was cotransfected into the TE671 cells with one of the following effector plasmids (1 μg): FGFR1, FGFR1(TM−), FGFR1(SP−), or control pcDNA3.1. The luciferase activity was measured 48 h later. The experiments were repeated two to four times. (D) Expression and transactivation of FGF-2 promoter by FGFR1(SP−/NLS). (Inset) TE671 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1FGFR1, pcDNA3.1FGFR1(SP−/NLS), or with control pcDNA3.1. Nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) fractions (Western blot with FGFR1 McAb6, 60 μg of protein per lane). Bar graph (−650/+314)FGF-2Luc (1 μg) was cotransfected with (1 μg) pcDNAFGFR1, pcDNAFGFR1(SP−/NLS), or control pcDNA3.1. The luciferase activity was measured 48 h later.