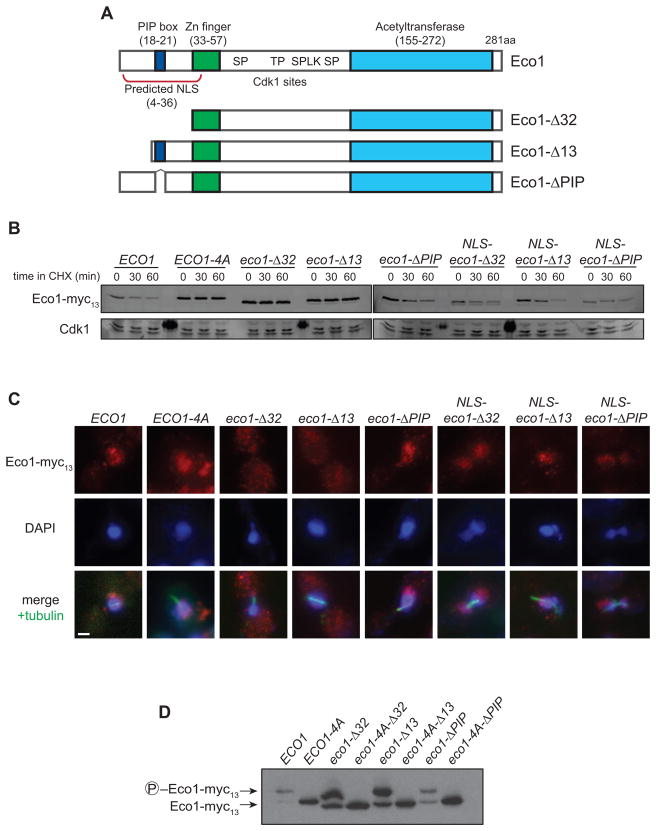
Figure 5. Eco1 contains a functional NLS that is necessary for its degradation.
(A) Diagram of known Eco1 protein domains; numbers indicate amino acid position. See Figure S1A for sequence of N-terminus.
(B) ECO1-myc13 strains containing the indicated N-terminal mutations were arrested in metaphase with nocodazole. After addition of cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times, lysates were analyzed by western blotting using fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies. All N-terminal truncations are wpl1Δ. ‘NLS’ indicates that the SV40 Large T antigen nuclear localization signal (PKKKRKVG) was inserted immediately after the start codon. Dark spots on the Cdk1 loading control are due to fluorescence of a molecular weight marker.
(C) Asynchronous ECO1-myc13 cultures were analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to Myc and alpha-tubulin, and stained for DNA using DAPI. Images from mitotic cells are shown (based on cell and spindle morphology, and DNA mass separation), and are representative of all cell cycle stages. Bar = 1 μm.
(D) Lysates of nocodazole-arrested cells were analyzed by Phos-tag-containing SDS-PAGE and western blotting.