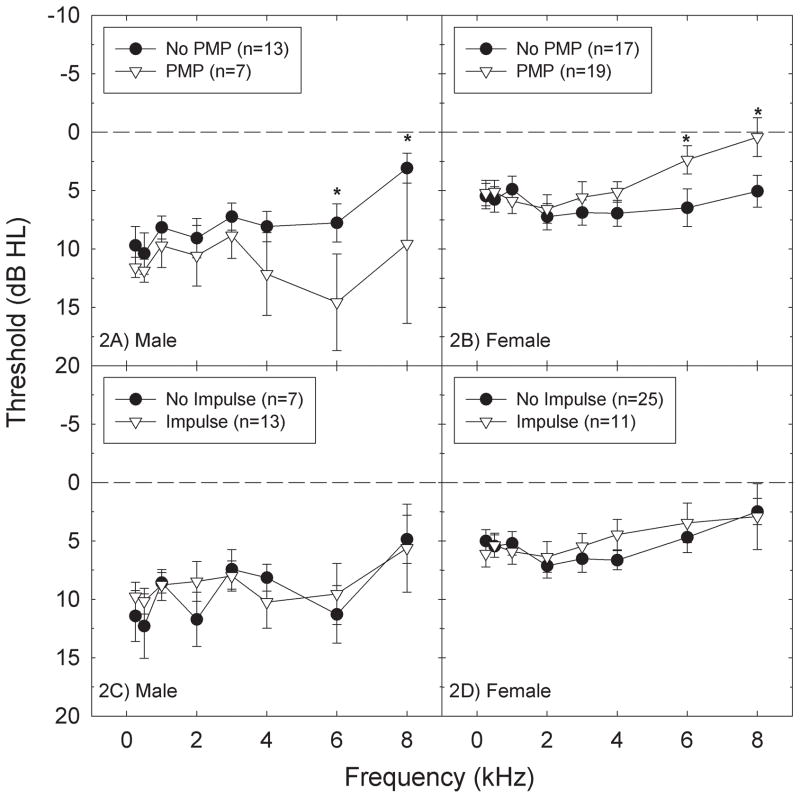
Figure 2.
Threshold sensitivity (mean +/− S.E.) significantly differed at only 6 kHz and 8 kHz as a function of reported PMP use in both male (2A) and female (2B) subjects. Male subjects that reported use of PMPs had significantly worse threshold sensitivity than male subjects that did not report use of PMPs; the opposite relationship was observed in female subjects. Threshold sensitivity (mean +/− S.E.) did not differ as a function of reported impulse noise exposure in either male (2C) or female (2D) subjects. One asterisk indicates statistically significant difference at the 0.05 level.